Politics
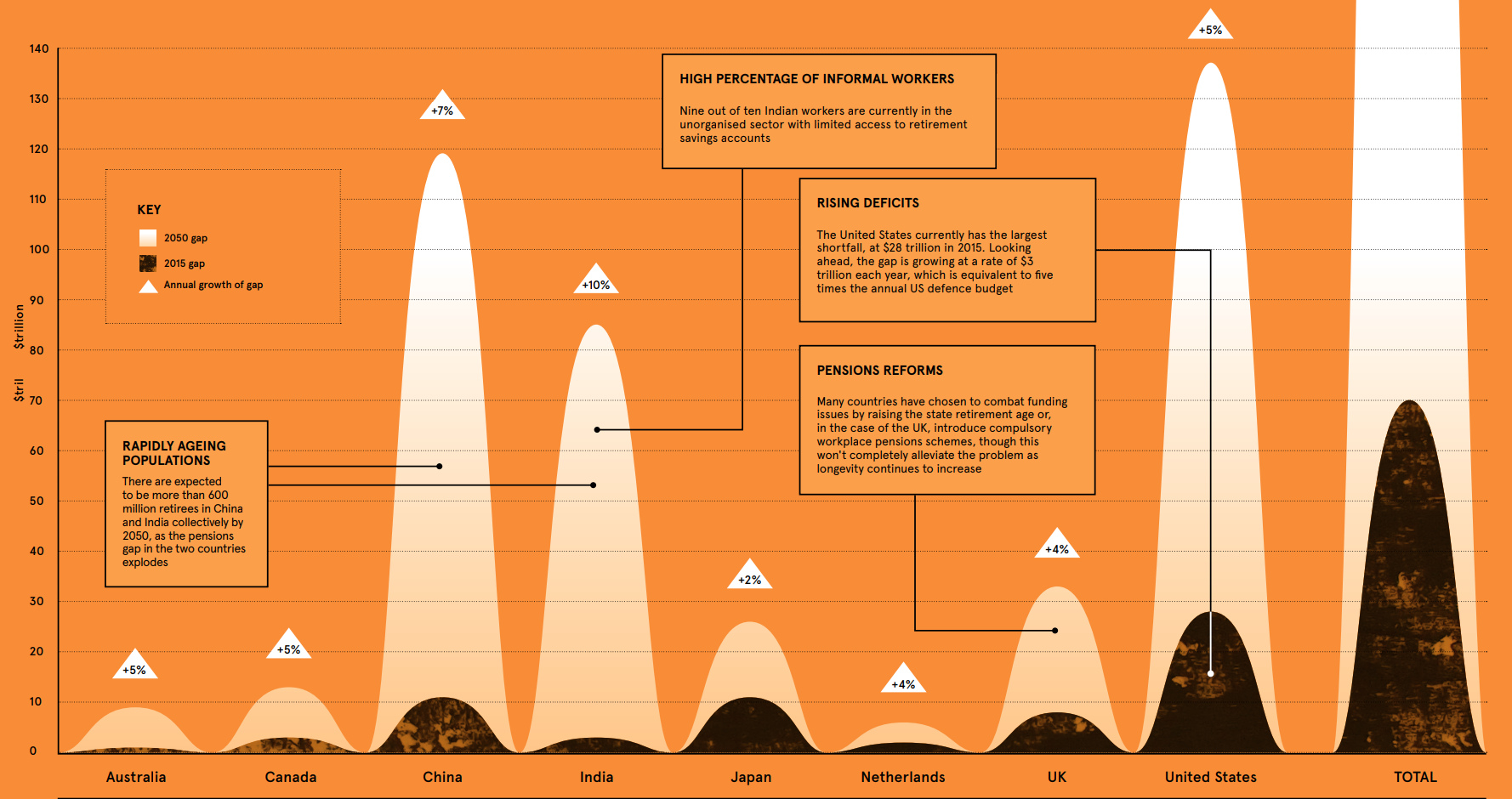
The Pension Time Bomb: $400 Trillion by 2050
View a high resolution version of this graphic
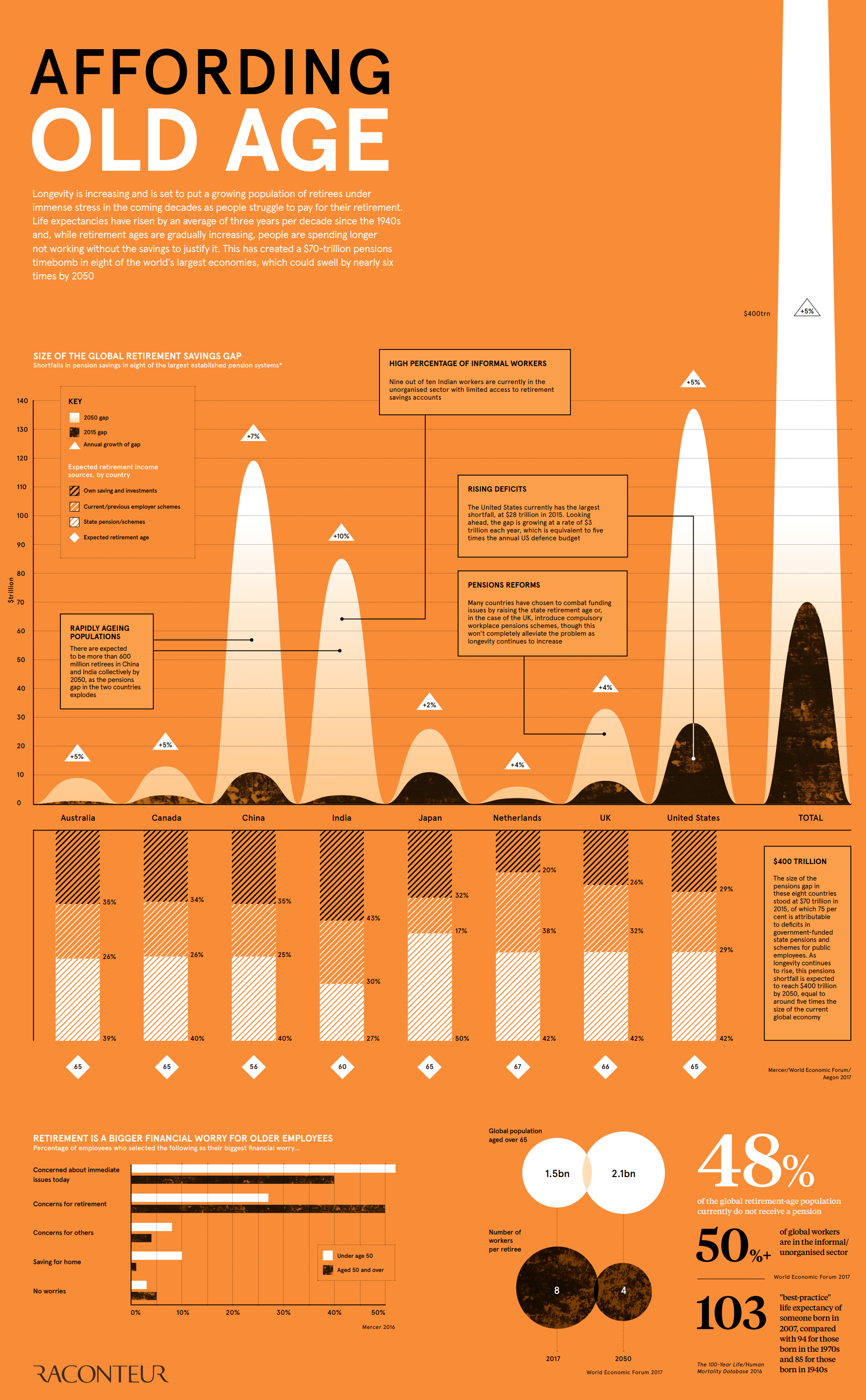
The Pension Time Bomb: $400 Trillion by 2050
View the high resolution version of today’s graphic by clicking here.
Are governments making promises about pensions that they might not be able to keep?
According to an analysis by the World Economic Forum (WEF), there was a combined retirement savings gap in excess of $70 trillion in 2015, spread between eight major economies..
The WEF says the deficit is growing by $28 billion every 24 hours – and if nothing is done to slow the growth rate, the deficit will reach $400 trillion by 2050, or about five times the size of the global economy today.
The group of economies studied: Canada, Australia, Netherlands, Japan, India, China, the United Kingdom, and the United States.
Mind the Gap
Today’s infographic comes to us from Raconteur, and it illuminates a growing problem attached to an aging population (and those that will be supporting it).
Since social security programs were initially developed, the circumstances around work and retirement have shifted considerably. Life expectancy has risen by three years per decade since the 1940s, and older people are having increasingly long life spans. With the retirement age hardly changing in most economies, this longevity means that people are spending longer not working without the savings to justify it.
This problem is amplified by the size of generations and fertility rates. The population of retirees globally is expected to grow from 1.5 billion to 2.1 billion between 2017-2050, while the number of workers for each retiree is expected to halve from eight to four over the same timeframe.
The WEF has made clear that the situation is not trivial, likening the scenario to “financial climate change”:
The anticipated increase in longevity and resulting ageing populations is the financial equivalent of climate change
Michael Drexler, Head of Financial and Infrastructure Systems, WEF
Like climate change, some of the early signs of this retirement savings gap can be “sandbagged” for the time being – but if not handled properly in the medium and long term, the adverse effects could be overwhelming.
Future Proofing
While implementing various system reforms like raising the retirement age will help, ultimately the money in the system has to come from somewhere. Social security programs will need to cut benefits, increase taxes, or borrow from somewhere else in the government’s budget to make up for the coming shortfalls.
In the United States specifically, it is expected that the Social Security trust fund will run out by 2034. At that point, there will only be enough revenue coming in to pay out approximately 77% of benefits.
United States
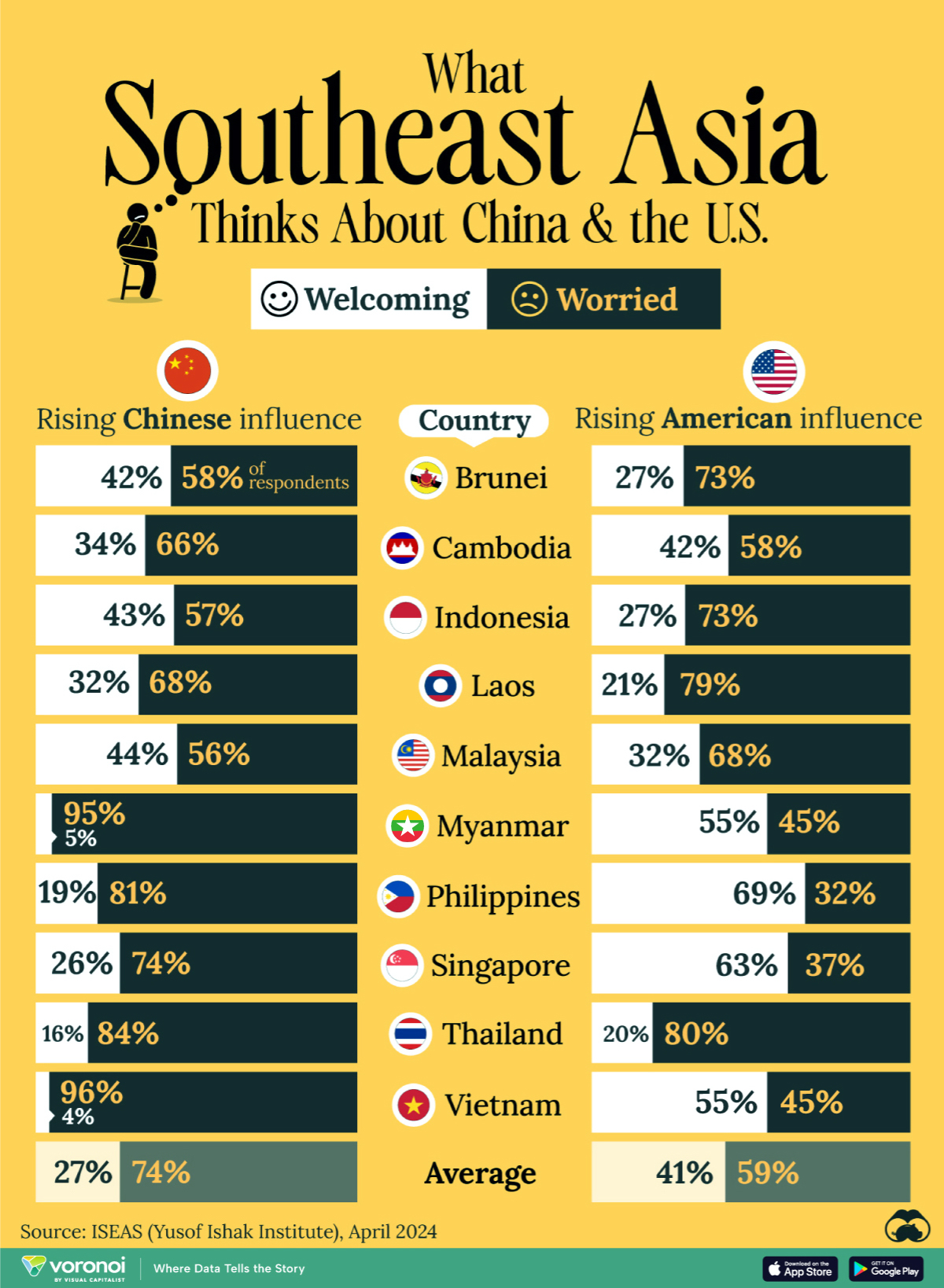
Charted: What Southeast Asia Thinks About China & the U.S.
A significant share of respondents from an ASEAN-focused survey are not happy about rising American and Chinese influence in the region.
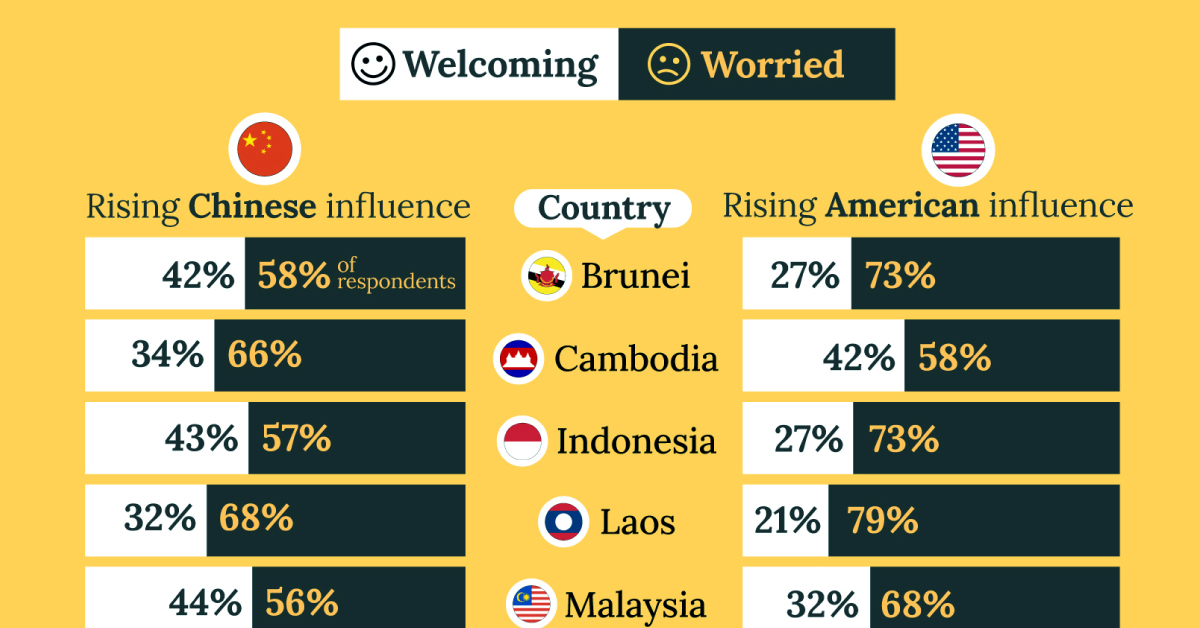
What Southeast Asia Thinks About China & the U.S.
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
This chart visualizes the results of a 2024 survey conducted by the ASEAN Studies Centre at the ISEAS-Yusof Ishak Institute. Nearly 2,000 respondents were asked if they were worried or welcoming of rising Chinese and American geopolitical influence in their country.
The countries surveyed all belong to the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN), a political and economic union of 10 states in Southeast Asia.
Feelings Towards China
On average, a significant share of respondents from all 10 countries are worried about rising influence from both the U.S. and China.
However, overall skepticism is higher for China, at 74% (versus 59% for U.S.).
| Country | Worried About Growing 🇨🇳 Influence | Welcome Growing 🇨🇳 Influence |
|---|---|---|
| 🇧🇳 Brunei | 58% | 42% |
| 🇰🇭 Cambodia | 66% | 34% |
| 🇮🇩 Indonesia | 57% | 43% |
| 🇱🇦 Laos | 68% | 32% |
| 🇲🇾 Malaysia | 56% | 44% |
| 🇲🇲 Myanmar | 95% | 5% |
| 🇵🇭 Philippines | 81% | 19% |
| 🇸🇬 Singapore | 74% | 26% |
| 🇹🇭 Thailand | 84% | 16% |
| 🇻🇳 Vietnam | 96% | 4% |
| Average | 74% | 27% |
The recently-cooled but still active territorial concerns over the South China Sea may play a significant role in these responses, especially in countries which are also claimants over the sea.
For example, in Vietnam over 95% of respondents said they were worried about China’s growing influence.
Feelings Towards America
Conversely, rising American influence is welcomed in two countries with competing claims in the South China Sea, the Philippines (69%) and Vietnam (55%).
| Country | Worried About Growing 🇺🇸 Influence | Welcome Growing 🇺🇸 Influence |
|---|---|---|
| 🇧🇳 Brunei | 73% | 27% |
| 🇰🇭 Cambodia | 58% | 42% |
| 🇮🇩 Indonesia | 73% | 27% |
| 🇱🇦 Laos | 79% | 21% |
| 🇲🇾 Malaysia | 68% | 32% |
| 🇲🇲 Myanmar | 45% | 55% |
| 🇵🇭 Philippines | 32% | 69% |
| 🇸🇬 Singapore | 37% | 63% |
| 🇹🇭 Thailand | 80% | 20% |
| 🇻🇳 Vietnam | 45% | 55% |
| Average | 59% | 41% |
Despite this, on a regional average, more respondents worry about growing American influence (59%) than they welcome it (41%).
Interestingly, it seems almost every ASEAN nation has a clear preference for one superpower over the other.
The only exception is Thailand, where those surveyed were not a fan of either option, with 84% worried about China, and 80% worried about the U.S.
-

 Culture6 days ago
Culture6 days agoThe World’s Top Media Franchises by All-Time Revenue
-

 Science2 weeks ago
Science2 weeks agoVisualizing the Average Lifespans of Mammals
-

 Brands2 weeks ago
Brands2 weeks agoHow Tech Logos Have Evolved Over Time
-

 Energy2 weeks ago
Energy2 weeks agoRanked: The Top 10 EV Battery Manufacturers in 2023
-

 Countries2 weeks ago
Countries2 weeks agoCountries With the Largest Happiness Gains Since 2010
-

 Economy2 weeks ago
Economy2 weeks agoVC+: Get Our Key Takeaways From the IMF’s World Economic Outlook
-

 Demographics1 week ago
Demographics1 week agoThe Countries That Have Become Sadder Since 2010
-

 Money1 week ago
Money1 week agoCharted: Who Has Savings in This Economy?