Technology
Explainer: How Synthetic Biology is Redesigning Life
Explainer: How Synthetic Biology is Redesigning Life
Synthetic biology (SynBio) is a field of science that involves engineering life for human benefit. It has the potential to reshape many facets of society—from the ways we produce food, to how we detect and cure diseases.
It’s a fast-growing field of science. In fact, by 2026, the SynBio market’s global revenue is expected to reach $34.5 billion, at a CAGR of 21.9%.
While this fascinating area of research is worth paying attention to, it might be daunting to wrap your head around—especially if you don’t come from a scientific background. With this in mind, here’s an introduction to synthetic biology, and how it works.
What is Synthetic Biology?
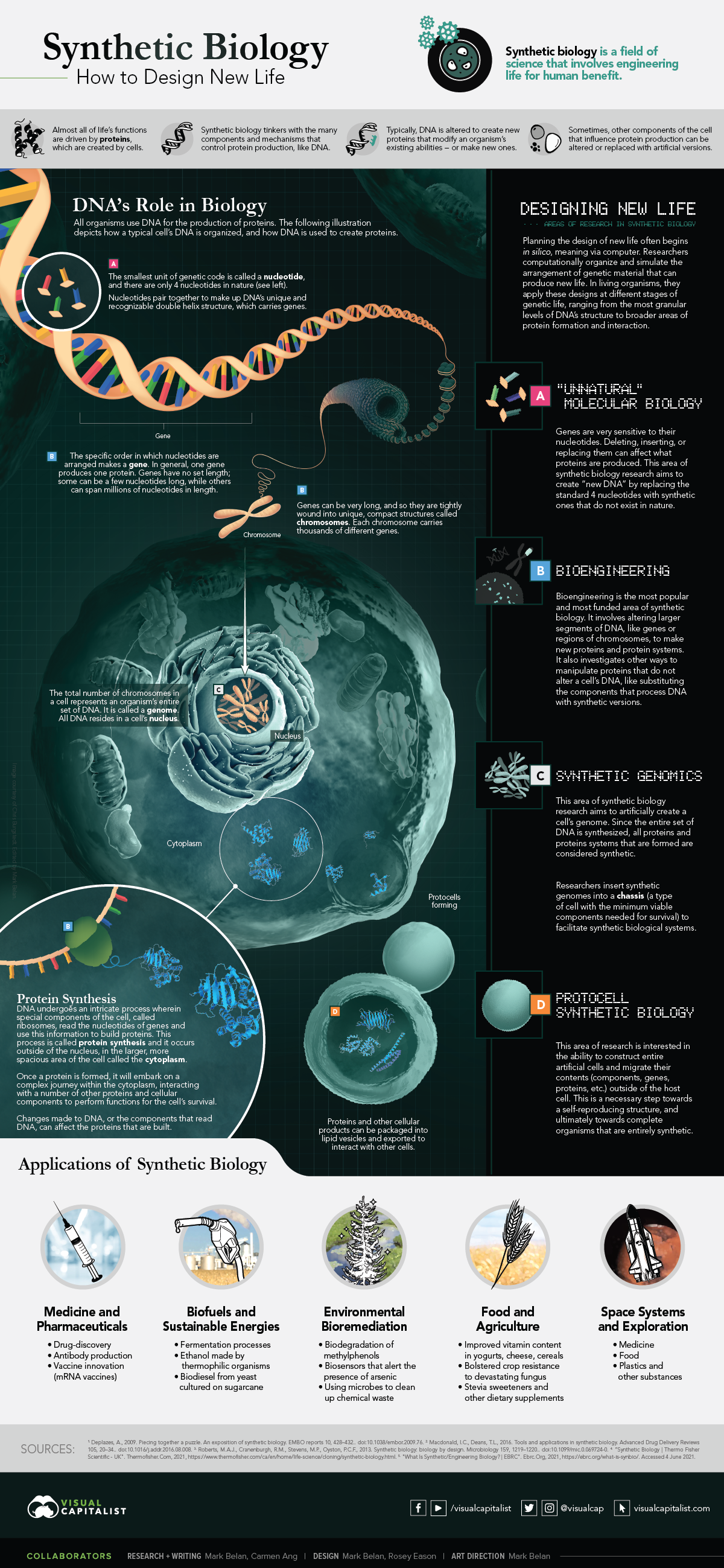
As we touched on in the introduction, SynBio is an area of scientific research that involves editing and redesigning the biological components, systems, and interactions that make up life. By doing this, SynBio can grant organisms new abilities that are beneficial to humans.
It’s similar to genetic engineering, however, it’s slightly more granular. While genetic engineering transfers ready-made genetic material between organisms, SynBio builds new genetic material from scratch.
SynBio has applications across a myriad of fields, with research covering everything from space exploration to drug discovery. Here’s a look at five of its real-world applications:
1. Medical Technologies
SynBio has a wide range of medical applications, including drug discovery, antibody production, and vaccine innovation (it’s been key in the fight against COVID-19). It also plays a significant role in “living drug” development, which is the use of living microbes to treat chronic or severe illnesses.
2. Sustainable Energies
Biofuel, which is renewable energy that’s derived from living matter, could replace petroleum and diesel in the near future—and synthetic biology technology is helping develop fermentation processes that will produce biofuel more efficiently.
3. Bioremediation
Bioremediation uses living organisms to restore polluted sites to their original condition. This field uses SynBio to try and make the decontamination process more efficient, and to expand the list of contaminants that bioremediation can target.
4. Food and Agriculture
SynBio plays a significant role in cellular agriculture, which is the production of agricultural products directly from cells rather than livestock or plants. These modified foods might have higher nutritional value, or might be void of allergens. For instance, this can be used to make plant-based burgers taste more like meat.
5. Space Systems and Exploration
Synthetic biology and 3-D printing have huge potential to sustain life during space exploration. Using SynBio technology, cells and bacteria could be modified to produce a myriad of materials—from plastic to medicine, and even food—and astronauts could print these synthetically engineered materials on-demand while in space.
Zooming in: the Science Behind Synthetic Biology
Now that we’ve touched on SynBio’s use in a wide range of industries, let’s dive into the science behind it. In order to understand the mechanics of SynBio, it’s important to explore the relationship between DNA and protein production.
Proteins are the drivers of life in a cell—they’re responsible for carrying out all of life’s functions. They are created through a process called protein synthesis, which relies heavily on DNA. Why is DNA so important in protein production? Because it houses all the information a cell needs for protein synthesis.
Once a protein is formed, it embarks on a complex journey throughout the cell, interacting with a number of other proteins and cellular components to perform functions needed for the cell’s survival.
This process of protein production and cellular interaction is an example of a biological system. And it’s this biological system that synthetic biologists investigate, and try to manipulate.
The Five Main Areas of Research
After combing through the literature, we identified five major areas of SynBio research:
- In silico Synthetic Biology
Meaning “via computer”, this area of SynBio research uses computational simulations to design and predict new biological systems. It’s like using a drawing board before starting a project. - “Unnatural” Molecular Biology
An area of research focused on altering the smallest unit of DNA—nucleotides. - Bioengineering
This area of research deals with larger segments of DNA like genes or chromosomes, and sometimes other cell components that interact with DNA. It aims to create new proteins or protein systems and is the most popular area of SynBio research. - Synthetic Genomics
Focused on altering and manipulating whole genomes (which is the complete set of a cell’s DNA). - Protocell Synthetic Biology
This field of research aims to construct whole cells. This is a step towards creating organisms that are entirely synthetic
While early research in SynBio struggled to finish real-world projects, innovation in this field has ramped up quickly in the last decade.
Synthetic biology products are becoming increasingly more pervasive in everyday life—so much so that by 2030, some scientists believe most people will have eaten, worn, or used something created through synthetic biology.
Technology
Ranked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
Nvidia is coming for Intel’s crown. Samsung is losing ground. AI is transforming the space. We break down revenue for semiconductor companies.
Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on Apple or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
Did you know that some computer chips are now retailing for the price of a new BMW?
As computers invade nearly every sphere of life, so too have the chips that power them, raising the revenues of the businesses dedicated to designing them.
But how did various chipmakers measure against each other last year?
We rank the biggest semiconductor companies by their percentage share of the industry’s revenues in 2023, using data from Omdia research.
Which Chip Company Made the Most Money in 2023?
Market leader and industry-defining veteran Intel still holds the crown for the most revenue in the sector, crossing $50 billion in 2023, or 10% of the broader industry’s topline.
All is not well at Intel, however, with the company’s stock price down over 20% year-to-date after it revealed billion-dollar losses in its foundry business.
| Rank | Company | 2023 Revenue | % of Industry Revenue |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Intel | $51B | 9.4% |
| 2 | NVIDIA | $49B | 9.0% |
| 3 | Samsung Electronics | $44B | 8.1% |
| 4 | Qualcomm | $31B | 5.7% |
| 5 | Broadcom | $28B | 5.2% |
| 6 | SK Hynix | $24B | 4.4% |
| 7 | AMD | $22B | 4.1% |
| 8 | Apple | $19B | 3.4% |
| 9 | Infineon Tech | $17B | 3.2% |
| 10 | STMicroelectronics | $17B | 3.2% |
| 11 | Texas Instruments | $17B | 3.1% |
| 12 | Micron Technology | $16B | 2.9% |
| 13 | MediaTek | $14B | 2.6% |
| 14 | NXP | $13B | 2.4% |
| 15 | Analog Devices | $12B | 2.2% |
| 16 | Renesas Electronics Corporation | $11B | 1.9% |
| 17 | Sony Semiconductor Solutions Corporation | $10B | 1.9% |
| 18 | Microchip Technology | $8B | 1.5% |
| 19 | Onsemi | $8B | 1.4% |
| 20 | KIOXIA Corporation | $7B | 1.3% |
| N/A | Others | $126B | 23.2% |
| N/A | Total | $545B | 100% |
Note: Figures are rounded. Totals and percentages may not sum to 100.
Meanwhile, Nvidia is very close to overtaking Intel, after declaring $49 billion of topline revenue for 2023. This is more than double its 2022 revenue ($21 billion), increasing its share of industry revenues to 9%.
Nvidia’s meteoric rise has gotten a huge thumbs-up from investors. It became a trillion dollar stock last year, and broke the single-day gain record for market capitalization this year.
Other chipmakers haven’t been as successful. Out of the top 20 semiconductor companies by revenue, 12 did not match their 2022 revenues, including big names like Intel, Samsung, and AMD.
The Many Different Types of Chipmakers
All of these companies may belong to the same industry, but they don’t focus on the same niche.
According to Investopedia, there are four major types of chips, depending on their functionality: microprocessors, memory chips, standard chips, and complex systems on a chip.
Nvidia’s core business was once GPUs for computers (graphics processing units), but in recent years this has drastically shifted towards microprocessors for analytics and AI.
These specialized chips seem to be where the majority of growth is occurring within the sector. For example, companies that are largely in the memory segment—Samsung, SK Hynix, and Micron Technology—saw peak revenues in the mid-2010s.
-

 Mining2 weeks ago
Mining2 weeks agoCharted: The Value Gap Between the Gold Price and Gold Miners
-

 Real Estate1 week ago
Real Estate1 week agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 AI1 week ago
AI1 week agoThe Stock Performance of U.S. Chipmakers So Far in 2024
-

 Misc1 week ago
Misc1 week agoAlmost Every EV Stock is Down After Q1 2024
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhere Does One U.S. Tax Dollar Go?
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoRanked: Top Countries by Total Forest Loss Since 2001
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoVisualizing America’s Shortage of Affordable Homes