Technology
The Global Fiber Optic Network Explained
The Global Fiber Optic Network Explained
As we scroll through Instagram or cue up another episode on Netflix, most of us give little thought to the hidden network of fiber optic cables that instantaneously shuttle information around the globe.
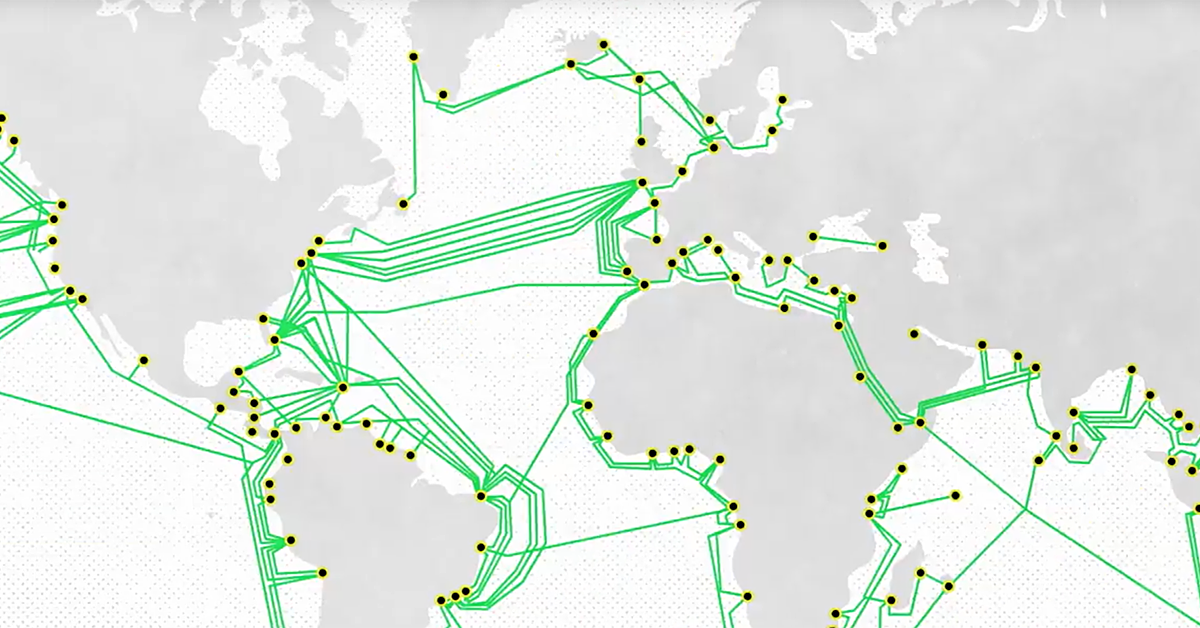
This extensive network of cables – which could stretch around the Equator 30 times – is the connective tissue that binds the internet, and thanks to our insatiable appetite for video streaming, it’s growing larger with every passing year.
Today’s video, by TED-Ed, explains how fiber optic cables work and introduces the next generation of cables that could drastically increase the speed of data transmission.
A Series of Tubes
The late Senator Ted Stevens drew laughter for describing the internet as a “series of tubes” in 2006, but as it turns out, most of the information moving around the world does, in fact, travel through a series of tubes. Undersea fiber optic tubes, to be exact.
The way this system functions is deceptively simple. Light, which is beamed into a fiber optic cable at a shallow angle, ricochets its way along the tube at close to light speed until being converted back into an electrical signal at its destination – generally a data center. To increase bandwidth further, some cables are able to carry multiple wavelengths concurrently.
Impressively, this simple method of bouncing light through a tube is what moves 99% of the world’s digital information.
The Glass Superhighway
Since the first undersea fiber optic cable, TAT-8, was constructed by a consortium of companies in 1988, the number of cables snaking across the ocean floor has risen dramatically. In fact, over 100 new cables will have been laid between 2016 and 2020, with a value of nearly $14 billion.
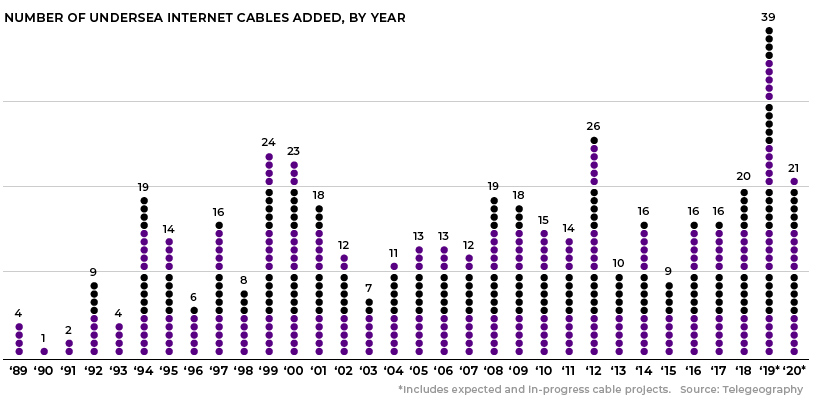
Increasing bandwidth requirements have transformed content providers from customers to cable owners. As a result, tech giants like Google and Facebook are taking a more active role in the expansion of the global fiber optic network. Google alone has at least five cable projects set for completion in 2019.
The Last Mile
Much like Amazon struggles with the “last mile” of deliveries, the transmission of digital information is much less efficient at the data center level, where servers are connected by traditional electric cables. These short-range cables are far less efficient than their fiber optic counterparts, losing half their running power as heat.
If this inefficient use of energy isn’t solved, internet-related activity could comprise a fifth of the world’s power consumption by 2030.
Thankfully, a related technology – integrated photonics – could keep the high-definition videos of the future streaming. Although the silicon wires used in integrated photonics do not guide light as effectively as fiber optics, the ultra-thin wires are far more compact. Photonic chips paired with burgeoning terahertz (THz) wireless communications could eventually form the backbone of a 6G network. Short-range THz signals would hitch a ride on silicon wires via tiny photonic chips scattered around population centers.
Before this efficient, high-capacity future is realized, researchers must first solve the puzzle of manufacturing photonic devices at scale. Once this method of data transmission hits the mainstream market, it could drastically alter the course of both computing and global energy consumption.
Technology
All of the Grants Given by the U.S. CHIPS Act
Intel, TSMC, and more have received billions in subsidies from the U.S. CHIPS Act in 2024.

All of the Grants Given by the U.S. CHIPS Act
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
This visualization shows which companies are receiving grants from the U.S. CHIPS Act, as of April 25, 2024. The CHIPS Act is a federal statute signed into law by President Joe Biden that authorizes $280 billion in new funding to boost domestic research and manufacturing of semiconductors.
The grant amounts visualized in this graphic are intended to accelerate the production of semiconductor fabrication plants (fabs) across the United States.
Data and Company Highlights
The figures we used to create this graphic were collected from a variety of public news sources. The Semiconductor Industry Association (SIA) also maintains a tracker for CHIPS Act recipients, though at the time of writing it does not have the latest details for Micron.
| Company | Federal Grant Amount | Anticipated Investment From Company |
|---|---|---|
| 🇺🇸 Intel | $8,500,000,000 | $100,000,000,000 |
| 🇹🇼 TSMC | $6,600,000,000 | $65,000,000,000 |
| 🇰🇷 Samsung | $6,400,000,000 | $45,000,000,000 |
| 🇺🇸 Micron | $6,100,000,000 | $50,000,000,000 |
| 🇺🇸 GlobalFoundries | $1,500,000,000 | $12,000,000,000 |
| 🇺🇸 Microchip | $162,000,000 | N/A |
| 🇬🇧 BAE Systems | $35,000,000 | N/A |
BAE Systems was not included in the graphic due to size limitations
Intel’s Massive Plans
Intel is receiving the largest share of the pie, with $8.5 billion in grants (plus an additional $11 billion in government loans). This grant accounts for 22% of the CHIPS Act’s total subsidies for chip production.
From Intel’s side, the company is expected to invest $100 billion to construct new fabs in Arizona and Ohio, while modernizing and/or expanding existing fabs in Oregon and New Mexico. Intel could also claim another $25 billion in credits through the U.S. Treasury Department’s Investment Tax Credit.
TSMC Expands its U.S. Presence
TSMC, the world’s largest semiconductor foundry company, is receiving a hefty $6.6 billion to construct a new chip plant with three fabs in Arizona. The Taiwanese chipmaker is expected to invest $65 billion into the project.
The plant’s first fab will be up and running in the first half of 2025, leveraging 4 nm (nanometer) technology. According to TrendForce, the other fabs will produce chips on more advanced 3 nm and 2 nm processes.
The Latest Grant Goes to Micron
Micron, the only U.S.-based manufacturer of memory chips, is set to receive $6.1 billion in grants to support its plans of investing $50 billion through 2030. This investment will be used to construct new fabs in Idaho and New York.
-

 Education1 week ago
Education1 week agoHow Hard Is It to Get Into an Ivy League School?
-

 Technology2 weeks ago
Technology2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries
-

 Economy2 weeks ago
Economy2 weeks agoWhere U.S. Inflation Hit the Hardest in March 2024
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoTop Countries By Forest Growth Since 2001