Energy
Visualizing the Biggest Risks to the Global Economy in 2020
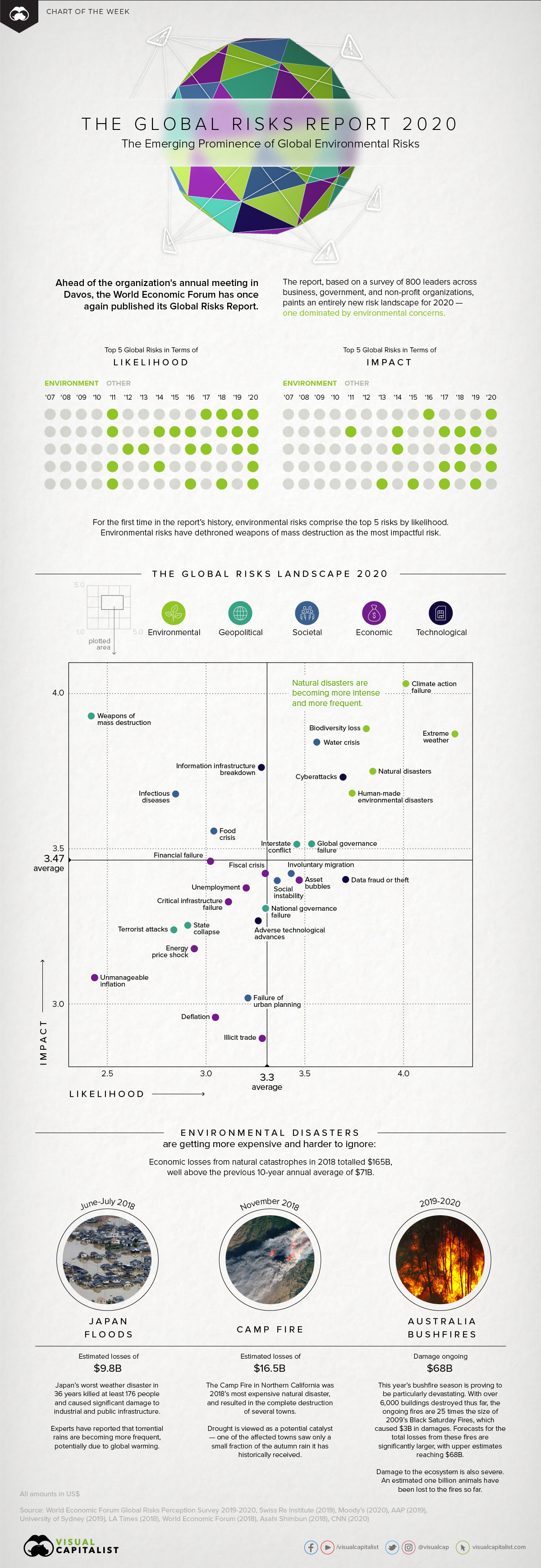
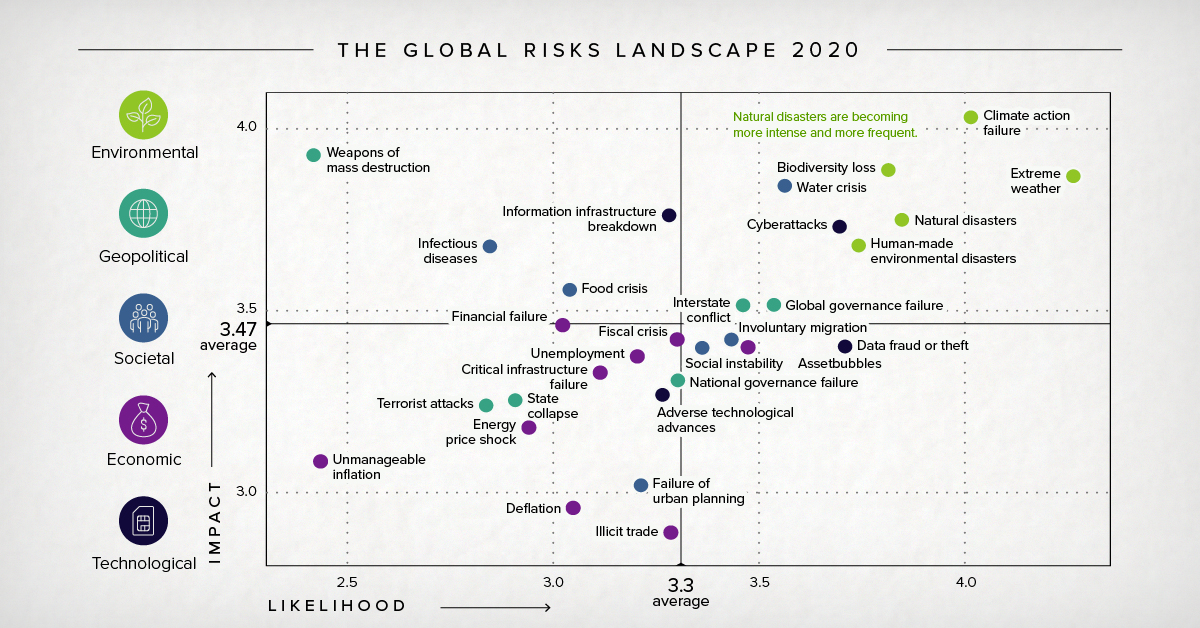
Top Risks in 2020: Dominated by Environmental Factors
Environmental concerns are a frequent talking point drawn upon by politicians and scientists alike, and for good reason. Irrespective of economic or social status, climate change has the potential to affect us all.
While public urgency surrounding climate action has been growing, it can be difficult to comprehend the potential extent of economic disruption that environmental risks pose.
Front and Center
Today’s chart uses data from the World Economic Forum’s annual Global Risks Report, which surveyed 800 leaders from business, government, and non-profits to showcase the most prominent economic risks the world faces.
According to the data in the report, here are the top five risks to the global economy, in terms of their likelihood and potential impact:
| Top Global Risks (by "Likelihood") | Top Global Risks (by "Impact") | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| #1 | Extreme weather | #1 | Climate action failure | |
| #2 | Climate action failure | #2 | Weapons of mass destruction | |
| #3 | Natural disasters | #3 | Biodiversity loss | |
| #4 | Biodiversity loss | #4 | Extreme weather | |
| #5 | Humanmade environmental disasters | #5 | Water crises | |
With more emphasis being placed on environmental risks, how much do we need to worry?
According to the World Economic Forum, more than we can imagine. The report asserts that, among many other things, natural disasters are becoming more intense and more frequent.
While it can be difficult to extrapolate precisely how environmental risks could cascade into trouble for the global economy and financial system, here are some interesting examples of how they are already affecting institutional investors and the insurance industry.
The Stranded Assets Dilemma
If the world is to stick to its 2°C global warming threshold, as outlined in the Paris Agreement, a significant amount of oil, gas, and coal reserves would need to be left untouched. These assets would become “stranded”, forfeiting roughly $1-4 trillion from the world economy.
Growing awareness of this risk has led to a change in sentiment. Many institutional investors have become wary of their portfolio exposures, and in some cases, have begun divesting from the sector entirely.
The financial case for fossil fuel divestment is strong. Fossil fuel companies once led the economy and world stock markets. They now lag.
– Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis
The last couple of years have been a game-changer for the industry’s future prospects. For example, 2018 was a milestone year in fossil fuel divestment:
- Nearly 1,000 institutional investors representing $6.24 trillion in assets have pledged to divest from fossil fuels, up from just $52 billion four years ago;
- Ireland became the first country to commit to fossil fuel divestment. At the time of announcement, its sovereign development fund had $10.4 billion in assets;
- New York City became the largest (but not the first) city to commit to fossil fuel divestment. Its pension funds, totaling $189 billion at the time of announcement, aim to divest over a 5-year period.
A Tough Road Ahead
In a recent survey, actuaries ranked climate change as their top risk for 2019, ahead of damages from cyberattacks, financial instability, and terrorism—drawing strong parallels with the results of this year’s Global Risk Report.
These growing concerns are well-founded. 2017 was the costliest year on record for natural disasters, with $344 billion in global economic losses. This daunting figure translated to a record year for insured losses, totalling $140 billion.
Although insured losses over 2019 have fallen back in line with the average over the past 10 years, Munich RE believes that long-term environmental effects are already being felt:
- Recent studies have shown that over the long term, the environmental conditions for bushfires in Australia have become more favorable;
- Despite a decrease in U.S. wildfire losses compared to previous years, there is a rising long-term trend for forest area burned in the U.S.;
- An increase in hailstorms, as a result of climate change, has been shown to contribute to growing losses across the globe.
The Ball Is In Our Court
It’s clear that the environmental issues we face are beginning to have a larger real impact. Despite growing awareness and preliminary actions such as fossil fuel divestment, the Global Risk Report stresses that there is much more work to be done to mitigate risks.
How companies and governments choose to respond over the next decade will be a focal point of many discussions to come.
Energy
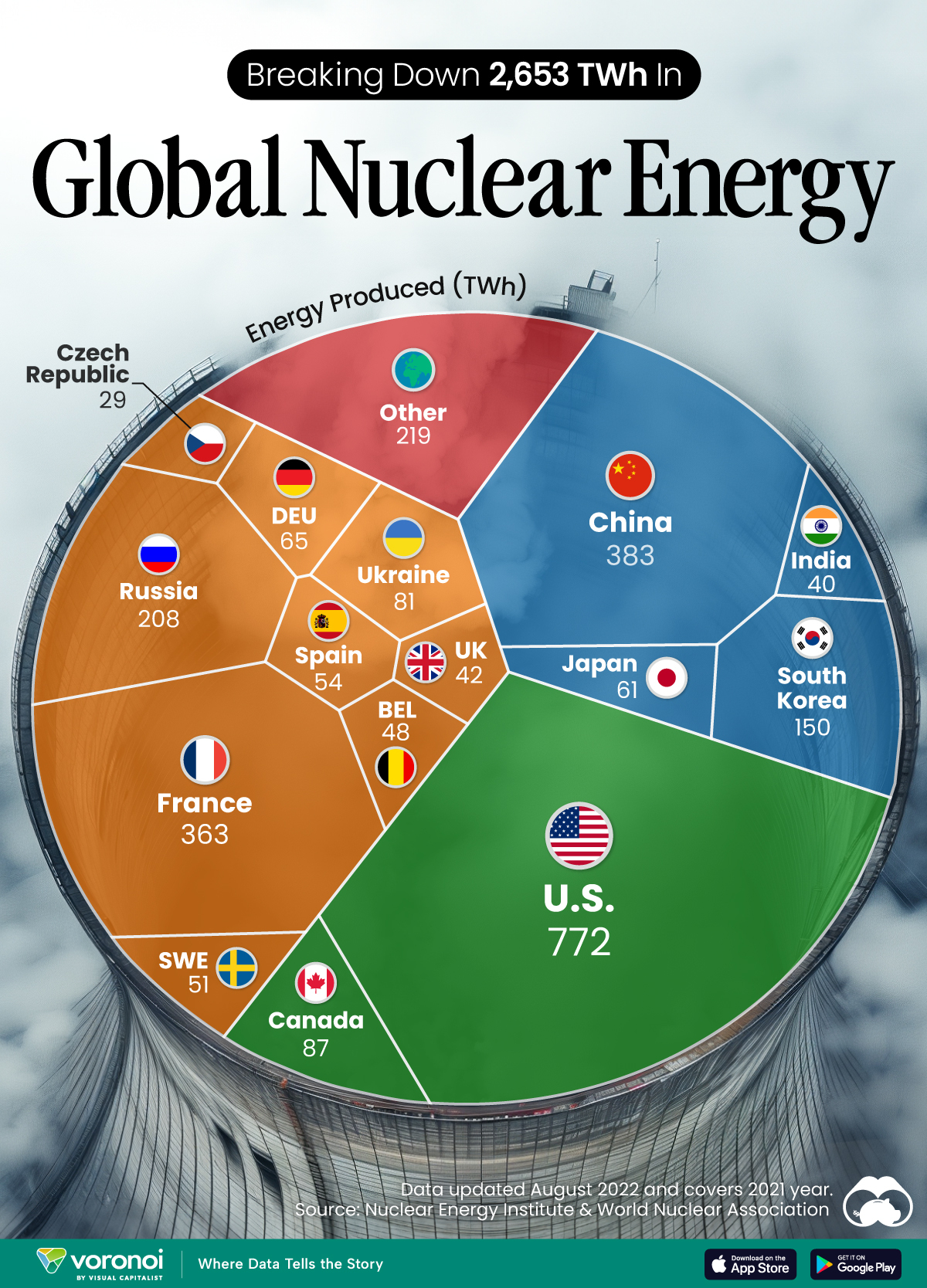
The World’s Biggest Nuclear Energy Producers
China has grown its nuclear capacity over the last decade, now ranking second on the list of top nuclear energy producers.

The World’s Biggest Nuclear Energy Producers
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on Apple or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
Scientists in South Korea recently broke a record in a nuclear fusion experiment. For 48 seconds, they sustained a temperature seven times that of the sun’s core.
But generating commercially viable energy from nuclear fusion still remains more science fiction than reality. Meanwhile, its more reliable sibling, nuclear fission, has been powering our world for many decades.
In this graphic, we visualized the top producers of nuclear energy by their share of the global total, measured in terawatt hours (TWh). Data for this was sourced from the Nuclear Energy Institute, last updated in August 2022.
Which Country Generates the Most Nuclear Energy?
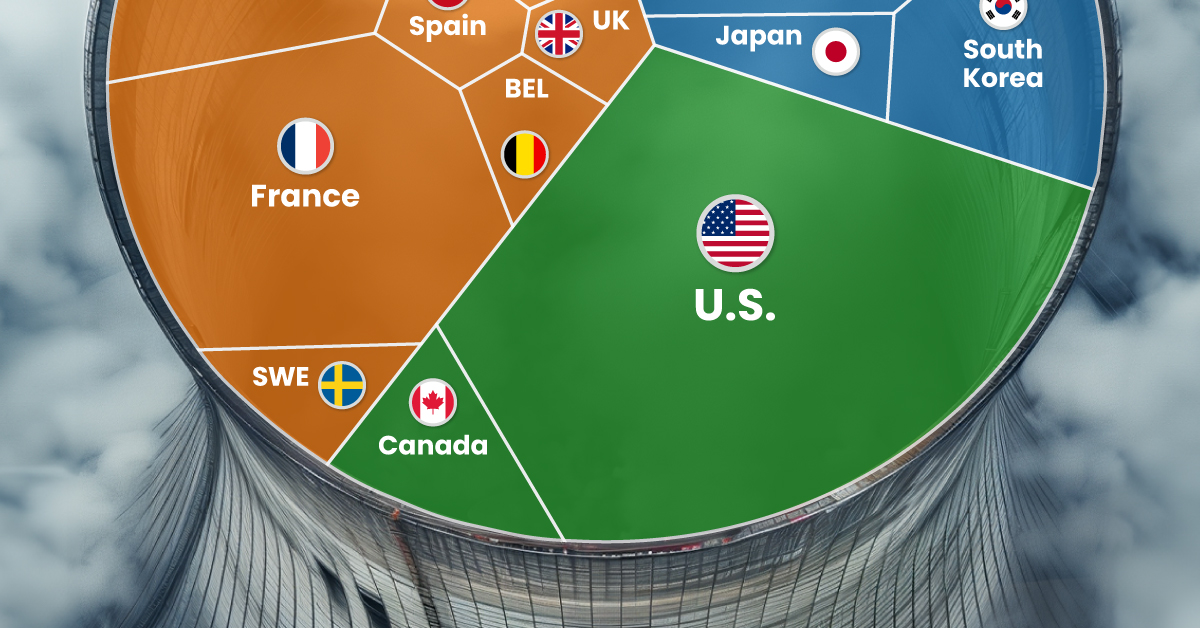
Nuclear energy production in the U.S. is more than twice the amount produced by China (ranked second) and France (ranked third) put together. In total, the U.S. accounts for nearly 30% of global nuclear energy output.
However, nuclear power only accounts for one-fifth of America’s electricity supply. This is in contrast to France, which generates 60% of its electricity from nuclear plants.
| Rank | Country | Nuclear Energy Produced (TWh) | % of Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 🇺🇸 U.S. | 772 | 29% |
| 2 | 🇨🇳 China | 383 | 14% |
| 3 | 🇫🇷 France | 363 | 14% |
| 4 | 🇷🇺 Russia | 208 | 8% |
| 5 | 🇰🇷 South Korea | 150 | 6% |
| 6 | 🇨🇦 Canada | 87 | 3% |
| 7 | 🇺🇦 Ukraine | 81 | 3% |
| 8 | 🇩🇪 Germany | 65 | 2% |
| 9 | 🇯🇵 Japan | 61 | 2% |
| 10 | 🇪🇸 Spain | 54 | 2% |
| 11 | 🇸🇪 Sweden | 51 | 2% |
| 12 | 🇧🇪 Belgium | 48 | 2% |
| 13 | 🇬🇧 UK | 42 | 2% |
| 14 | 🇮🇳 India | 40 | 2% |
| 15 | 🇨🇿 Czech Republic | 29 | 1% |
| N/A | 🌐 Other | 219 | 8% |
| N/A | 🌍 Total | 2,653 | 100% |
Another highlight is how China has rapidly grown its nuclear energy capabilities in the last decade. Between 2016 and 2021, for example, it increased its share of global nuclear energy output from less than 10% to more than 14%, overtaking France for second place.
On the opposite end, the UK’s share has slipped to 2% over the same time period.
Meanwhile, Ukraine has heavily relied on nuclear energy to power its grid. In March 2022, it lost access to its key Zaporizhzhia Nuclear Power Station after Russian forces wrested control of the facility. With six 1,000 MW reactors, the plant is one of the largest in Europe. It is currently not producing any power, and has been the site of recent drone attacks.
-

 Mining2 weeks ago
Mining2 weeks agoCharted: The Value Gap Between the Gold Price and Gold Miners
-

 Real Estate1 week ago
Real Estate1 week agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 AI1 week ago
AI1 week agoThe Stock Performance of U.S. Chipmakers So Far in 2024
-

 Misc1 week ago
Misc1 week agoAlmost Every EV Stock is Down After Q1 2024
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhere Does One U.S. Tax Dollar Go?
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoRanked: Top Countries by Total Forest Loss Since 2001
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoVisualizing America’s Shortage of Affordable Homes