Technology
Visualizing the Size of Amazon, the World’s Most Valuable Retailer
Visualizing the Size of the World’s Most Valuable Retailer
As brick-and-mortar chains teeter in the face of the pandemic, Amazon continues to gain ground.
The retail juggernaut is valued at no less than $1.4 trillion—roughly four times what it was in late 2016 when its market cap hovered around $350 billion. Last year, the Jeff Bezos-led company shipped 2 billion packages around the world.
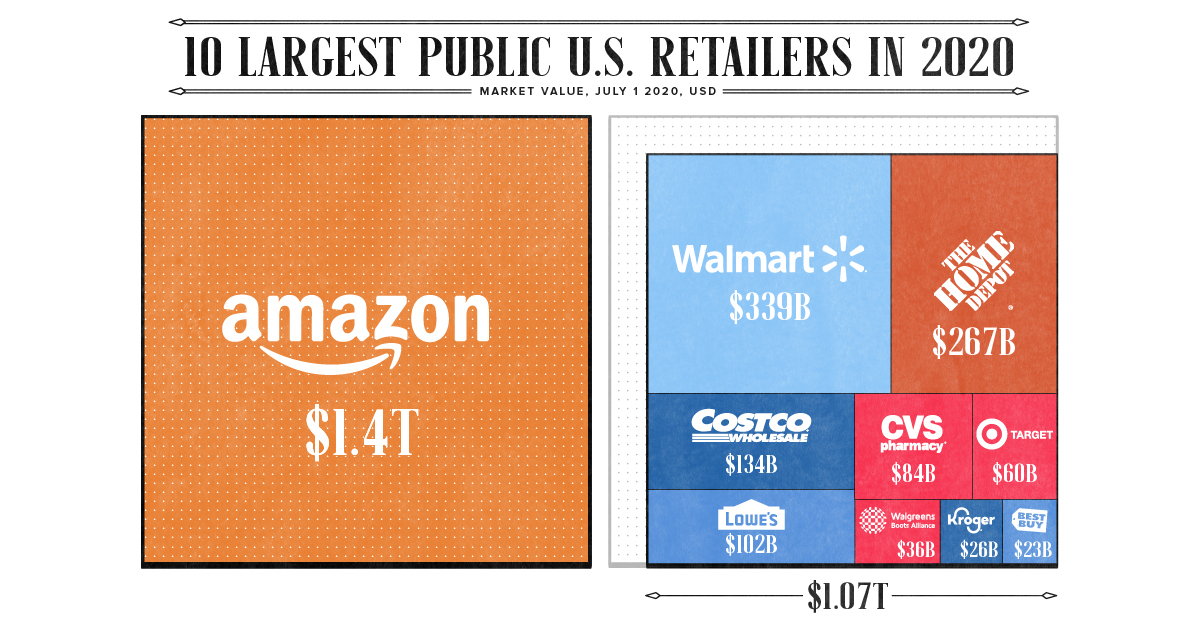
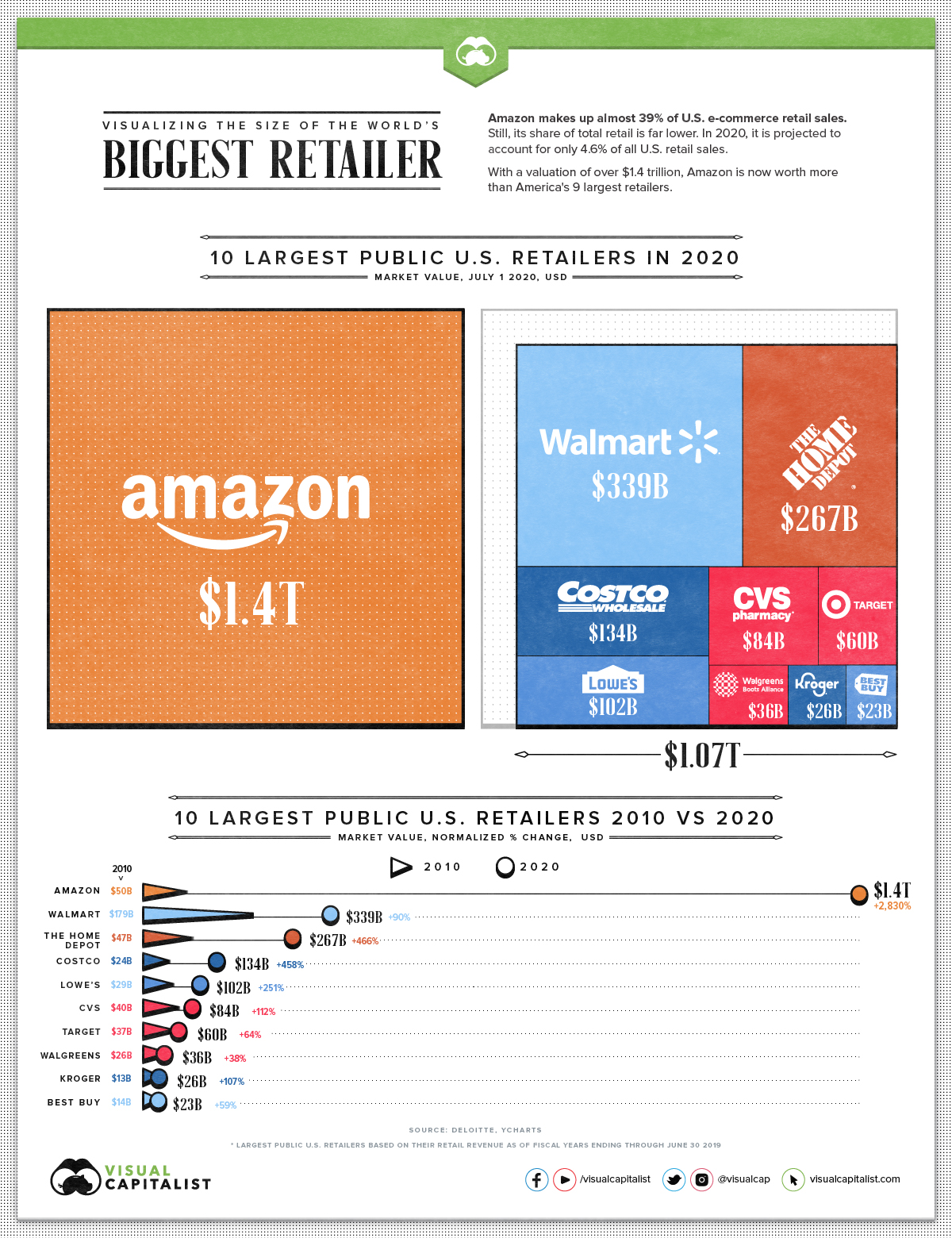
Today’s infographic shows how Amazon’s market cap alone is bigger than the nine biggest U.S. retailers put together, highlighting the palpable presence of the once modest online bookstore.
The New Normal
COVID-19’s sudden shift has rendered many retail outfits obsolete.
Neiman Marcus, JCPenney, and J.Crew have all filed for bankruptcy as consumer spending has migrated online. This, coupled with heavy debt loads across many retail chains, is only compounding the demise of brick-and-mortar. In fact, one estimate projects that at least 25,000 U.S. stores will fold over the next year.
Still, as safety and supply chain challenges mount—with COVID-19 related costs in the billions—Amazon remains at the top. It surpasses its next closest competitor, Walmart, by $1 trillion in market valuation.
How does Amazon compare to the largest retailers in the U.S.?
| 10 Largest Public US Retailers* | Market Value July 1, 2020 | Market Value July 1, 2010 | Normalized % Change 2010-2020 | Retail Revenue |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Walmart | $339B | $179B | 90% | $514B |
| Costco | $134B | $24B | 458% | $142B |
| Amazon | $1,400B | $50B | 2,830% | $140B |
| The Kroger Co. | $26B | $13B | 107% | $118Be |
| Walgreens Boots Alliance | $36B | $26B | 38% | $111B |
| The Home Depot | $267B | $47B | 466% | $108B |
| CVS | $84B | $40B | 112% | $84B |
| Target | $60B | $37B | 64% | $74B |
| Lowe's | $102B | $29B | 251% | $71B |
| Best Buy | $23B | $14B | 59% | $43B |
| Combined value of retailers (without Amazon) | $1,071B |
Source: Deloitte, YCharts
*Largest public US retailers based on their retail revenue as of fiscal years ending through June 30, 2019, e=estimated
With nearly a 39% share of U.S. e-commerce retail sales, Amazon’s market cap has grown 2,830% over the last decade. Its business model, which aggressively pursues market dominance instead of focusing on short-term profits, is one factor behinds the rise.
By the same token, one recent estimate by The Economist pegged Amazon’s retail operating margins at -1% last year. Another analyst has suggested that the company purposefully sells retail goods at a loss.
How Amazon makes up for this operating shortfall is through its cash-generating cloud service, Amazon Web Services (AWS), and through a collection of diversified enterprise-focused services. AWS, with estimated operating margins of 26%, brought in $9.2 billion in profits in 2019—more than half of Amazon’s total.
Amazon’s Basket of Eggs
Unlike many of its retail competitors, Amazon has rapidly diversified its acquisitions since it originated in 1994.
Take the $1.2 billion acquisition of Zoox. Amazon plans to operate self-driving taxi fleets, all of which are designed without steering wheels. It is the company’s third largest since the $13.7 billion acquisition of organic grocer Whole Foods, followed by Zappos.
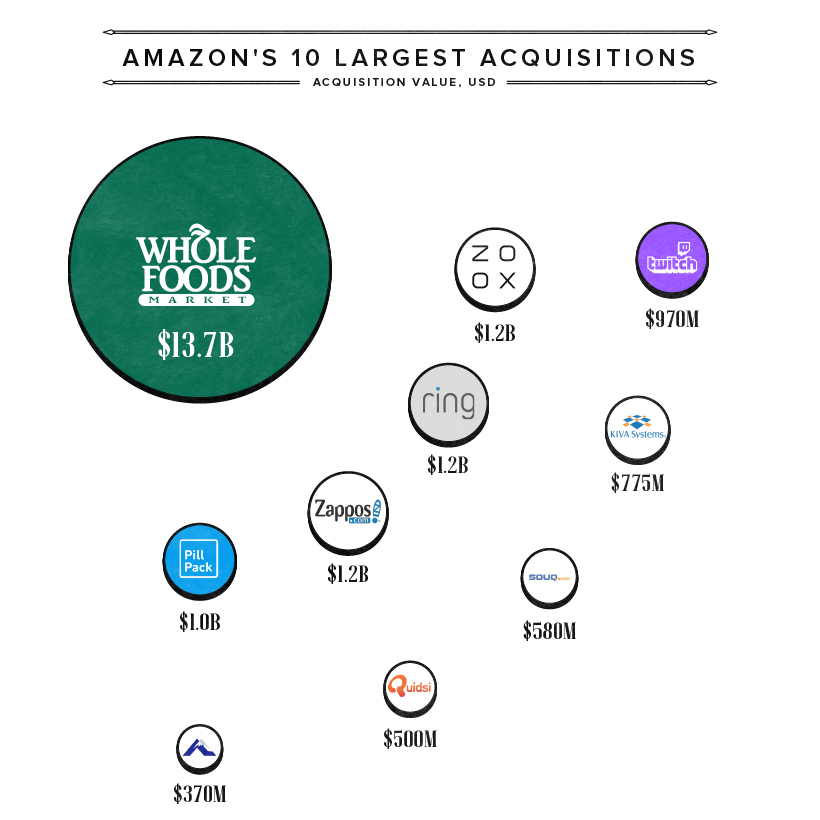
Accounting for the lion’s share of Amazon-owned physical stores, Whole Foods has 508 stores across the U.S., UK, and Canada. While Amazon doesn’t outline revenues across its physical retail segments—which include Amazon Books stores, Amazon Go stores, and others—physical store sales tipped over $17 billion in 2019.
Meanwhile, Amazon also owns gaming streaming platform Twitch, which it acquired for $970 million in 2017. Currently, Twitch makes up 73% of the streaming market and brought in an estimated $300 million in ad revenues in 2019.
Carrying On
Despite the flood of online orders due to quarantines and social distancing requirements, Amazon’s bottom line has suffered. In the second quarter of 2020 alone, it is expected to rack up $4 billion in pandemic-related costs.
Yet, at the same time, its customer-obsessed business model appears to thrive under current market conditions. As of July 1, its stock price has spiked over 51% year-to-date. On an annualized basis, that’s roughly 100% in returns.
As margins get squeezed and expenses grow, is Amazon’s growth sustainable in the long-term? Or, are the company’s strategic acquisitions and revenue streams providing the catalysts (and cash) for only more short-term success?
Technology
Ranked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
Nvidia is coming for Intel’s crown. Samsung is losing ground. AI is transforming the space. We break down revenue for semiconductor companies.
Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on Apple or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
Did you know that some computer chips are now retailing for the price of a new BMW?
As computers invade nearly every sphere of life, so too have the chips that power them, raising the revenues of the businesses dedicated to designing them.
But how did various chipmakers measure against each other last year?
We rank the biggest semiconductor companies by their percentage share of the industry’s revenues in 2023, using data from Omdia research.
Which Chip Company Made the Most Money in 2023?
Market leader and industry-defining veteran Intel still holds the crown for the most revenue in the sector, crossing $50 billion in 2023, or 10% of the broader industry’s topline.
All is not well at Intel, however, with the company’s stock price down over 20% year-to-date after it revealed billion-dollar losses in its foundry business.
| Rank | Company | 2023 Revenue | % of Industry Revenue |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Intel | $51B | 9.4% |
| 2 | NVIDIA | $49B | 9.0% |
| 3 | Samsung Electronics | $44B | 8.1% |
| 4 | Qualcomm | $31B | 5.7% |
| 5 | Broadcom | $28B | 5.2% |
| 6 | SK Hynix | $24B | 4.4% |
| 7 | AMD | $22B | 4.1% |
| 8 | Apple | $19B | 3.4% |
| 9 | Infineon Tech | $17B | 3.2% |
| 10 | STMicroelectronics | $17B | 3.2% |
| 11 | Texas Instruments | $17B | 3.1% |
| 12 | Micron Technology | $16B | 2.9% |
| 13 | MediaTek | $14B | 2.6% |
| 14 | NXP | $13B | 2.4% |
| 15 | Analog Devices | $12B | 2.2% |
| 16 | Renesas Electronics Corporation | $11B | 1.9% |
| 17 | Sony Semiconductor Solutions Corporation | $10B | 1.9% |
| 18 | Microchip Technology | $8B | 1.5% |
| 19 | Onsemi | $8B | 1.4% |
| 20 | KIOXIA Corporation | $7B | 1.3% |
| N/A | Others | $126B | 23.2% |
| N/A | Total | $545B | 100% |
Note: Figures are rounded. Totals and percentages may not sum to 100.
Meanwhile, Nvidia is very close to overtaking Intel, after declaring $49 billion of topline revenue for 2023. This is more than double its 2022 revenue ($21 billion), increasing its share of industry revenues to 9%.
Nvidia’s meteoric rise has gotten a huge thumbs-up from investors. It became a trillion dollar stock last year, and broke the single-day gain record for market capitalization this year.
Other chipmakers haven’t been as successful. Out of the top 20 semiconductor companies by revenue, 12 did not match their 2022 revenues, including big names like Intel, Samsung, and AMD.
The Many Different Types of Chipmakers
All of these companies may belong to the same industry, but they don’t focus on the same niche.
According to Investopedia, there are four major types of chips, depending on their functionality: microprocessors, memory chips, standard chips, and complex systems on a chip.
Nvidia’s core business was once GPUs for computers (graphics processing units), but in recent years this has drastically shifted towards microprocessors for analytics and AI.
These specialized chips seem to be where the majority of growth is occurring within the sector. For example, companies that are largely in the memory segment—Samsung, SK Hynix, and Micron Technology—saw peak revenues in the mid-2010s.
-

 Maps2 weeks ago
Maps2 weeks agoMapped: Average Wages Across Europe
-

 Money1 week ago
Money1 week agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 Real Estate1 week ago
Real Estate1 week agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Markets1 week ago
Markets1 week agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 AI1 week ago
AI1 week agoThe Stock Performance of U.S. Chipmakers So Far in 2024
-

 Automotive2 weeks ago
Automotive2 weeks agoAlmost Every EV Stock is Down After Q1 2024
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhere Does One U.S. Tax Dollar Go?
-

 Green2 weeks ago
Green2 weeks agoRanked: Top Countries by Total Forest Loss Since 2001

 Can I share this graphic?
Can I share this graphic? When do I need a license?
When do I need a license? Interested in this piece?
Interested in this piece?