Markets
Visualizing the 700-Year Fall of Interest Rates
Visualizing the 700-Year Decline of Interest Rates
How far can interest rates fall?
Currently, many sovereign rates sit in negative territory, and there is an unprecedented $10 trillion in negative-yielding debt. This new interest rate climate has many observers wondering where the bottom truly lies.
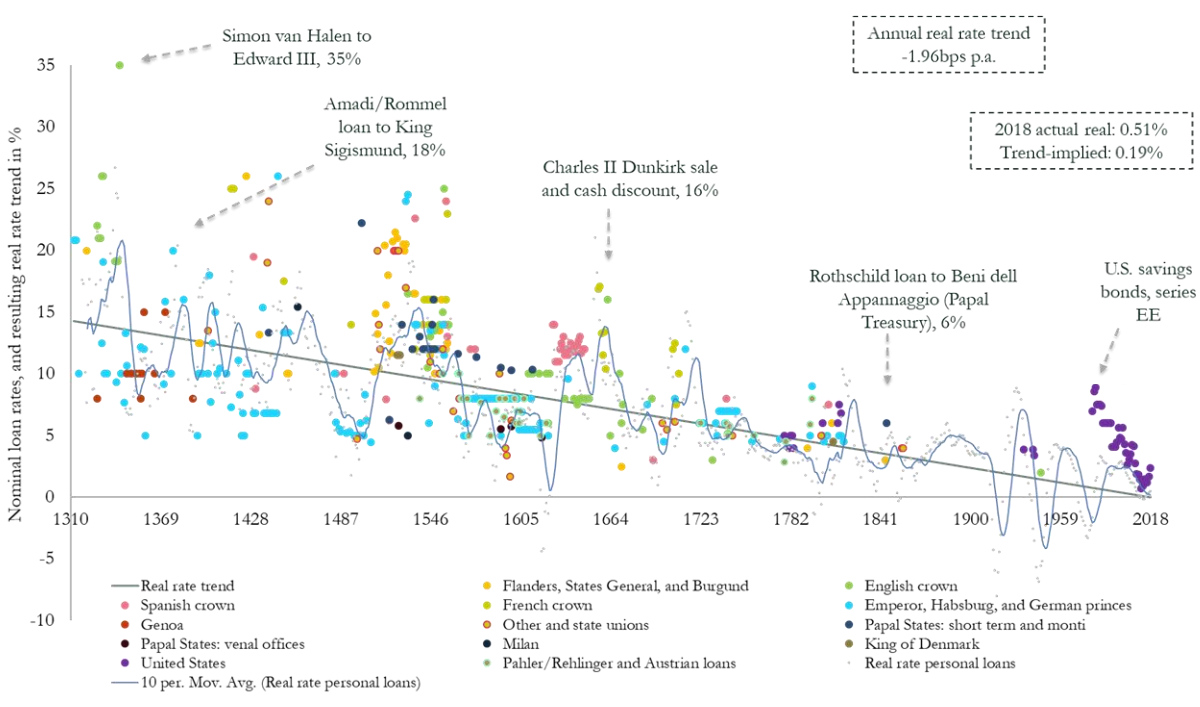
Today’s graphic from Paul Schmelzing, visiting scholar at the Bank of England (BOE), shows how global real interest rates have experienced an average annual decline of -0.0196% (-1.96 basis points) throughout the past eight centuries.
The Evidence on Falling Rates
Collecting data from across 78% of total advanced economy GDP over the time frame, Schmelzing shows that real rates* have witnessed a negative historical slope spanning back to the 1300s.
Displayed across the graph is a series of personal nominal loans made to sovereign establishments, along with their nominal loan rates. Some from the 14th century, for example, had nominal rates of 35%. By contrast, key nominal loan rates had fallen to 6% by the mid 1800s.
Centennial Averages of Real Long-Term “Safe-Asset”† Rates From 1311-2018
| % | 1300s | 1400s | 1500s | 1600s | 1700s | 1800s | 1900s | 2000s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nominal rate | 7.3 | 11.2 | 7.8 | 5.4 | 4.1 | 3.5 | 5.0 | 3.5 |
| Inflation | 2.2 | 2.1 | 1.7 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 3.1 | 2.2 |
| Real rate | 5.1 | 9.1 | 6.1 | 4.6 | 3.5 | 3.4 | 2.0 | 1.3 |
*Real rates take inflation into account, and are calculated as follows: nominal rate – inflation = real rate.
†Safe assets are issued from global financial powers
Starting in 1311, data from the report shows how average real rates moved from 5.1% in the 1300s down to an average of 2% in the 1900s.
The average real rate between 2000-2018 stands at 1.3%.
Current Theories
Why have interest rates been trending downward for so long?
Here are the three prevailing theories as to why they’re dropping:
1. Productivity Growth
Since 1970, productivity growth has slowed. A nation’s productive capacity is determined by a number of factors, including labor force participation and economic output.
If total economic output shrinks, real rates will decline too, theory suggests. Lower productivity growth leads to lower wage growth expectations.
In addition, lower productivity growth means less business investment, therefore a lower demand for capital. This in turn causes the lower interest rates.
2. Demographics
Demographics impact interest rates on a number of levels. The aging population—paired with declining fertility levels—result in higher savings rates, longer life expectancies, and lower labor force participation rates.
In the U.S., baby boomers are retiring at a pace of 10,000 people per day, and other advanced economies are also seeing comparable growth in retirees. Theory suggests that this creates downward pressure on real interest rates, as the number of people in the workforce declines.
3. Economic Growth
Dampened economic growth can also have a negative impact on future earnings, pushing down the real interest rate in the process. Since 1961, GDP growth among OECD countries has dropped from 4.3% to 3% in 2018.
Larry Summers referred to this sloping trend since the 1970s as “secular stagnation” during an International Monetary Fund conference in 2013.
Secular stagnation occurs when the economy is faced with persistently lagging economic health. One possible way to address a declining interest rate conundrum, Summers has suggested, is through expansionary government spending.
Bond Yields Declining
According to the report, another trend has coincided with falling interest rates: declining bond yields.
Since the 1300s, global nominal bonds yields have dropped from over 14% to around 2%.
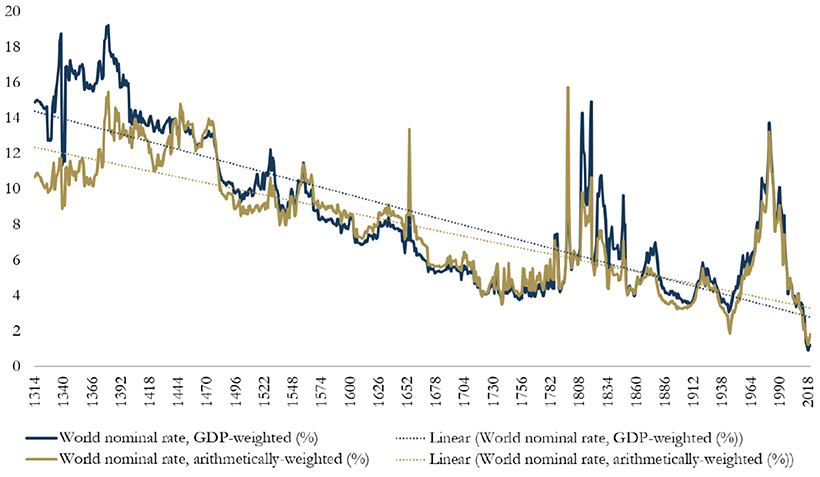
The graph illustrates how real interest rates and bond yields appear to slope across a similar trend line. While it may seem remarkable that interest rates keep falling, this phenomenon shows that a broader trend may be occurring—across centuries, asset classes, and fiscal regimes.
In fact, the historical record would imply that we will see ever new record lows in real rates in future business cycles in the 2020s/30s
-Paul Schmelzing
Although this may be fortunate for debt-seekers, it can create challenges for fixed income investors—who may seek alternatives strategies with higher yield potential instead.
Economy
Economic Growth Forecasts for G7 and BRICS Countries in 2024
The IMF has released its economic growth forecasts for 2024. How do the G7 and BRICS countries compare?

G7 & BRICS Real GDP Growth Forecasts for 2024
The International Monetary Fund’s (IMF) has released its real gross domestic product (GDP) growth forecasts for 2024, and while global growth is projected to stay steady at 3.2%, various major nations are seeing declining forecasts.
This chart visualizes the 2024 real GDP growth forecasts using data from the IMF’s 2024 World Economic Outlook for G7 and BRICS member nations along with Saudi Arabia, which is still considering an invitation to join the bloc.
Get the Key Insights of the IMF’s World Economic Outlook
Want a visual breakdown of the insights from the IMF’s 2024 World Economic Outlook report?
This visual is part of a special dispatch of the key takeaways exclusively for VC+ members.
Get the full dispatch of charts by signing up to VC+.
Mixed Economic Growth Prospects for Major Nations in 2024
Economic growth projections by the IMF for major nations are mixed, with the majority of G7 and BRICS countries forecasted to have slower growth in 2024 compared to 2023.
Only three BRICS-invited or member countries, Saudi Arabia, the UAE, and South Africa, have higher projected real GDP growth rates in 2024 than last year.
| Group | Country | Real GDP Growth (2023) | Real GDP Growth (2024P) |
|---|---|---|---|
| G7 | 🇺🇸 U.S. | 2.5% | 2.7% |
| G7 | 🇨🇦 Canada | 1.1% | 1.2% |
| G7 | 🇯🇵 Japan | 1.9% | 0.9% |
| G7 | 🇫🇷 France | 0.9% | 0.7% |
| G7 | 🇮🇹 Italy | 0.9% | 0.7% |
| G7 | 🇬🇧 UK | 0.1% | 0.5% |
| G7 | 🇩🇪 Germany | -0.3% | 0.2% |
| BRICS | 🇮🇳 India | 7.8% | 6.8% |
| BRICS | 🇨🇳 China | 5.2% | 4.6% |
| BRICS | 🇦🇪 UAE | 3.4% | 3.5% |
| BRICS | 🇮🇷 Iran | 4.7% | 3.3% |
| BRICS | 🇷🇺 Russia | 3.6% | 3.2% |
| BRICS | 🇪🇬 Egypt | 3.8% | 3.0% |
| BRICS-invited | 🇸🇦 Saudi Arabia | -0.8% | 2.6% |
| BRICS | 🇧🇷 Brazil | 2.9% | 2.2% |
| BRICS | 🇿🇦 South Africa | 0.6% | 0.9% |
| BRICS | 🇪🇹 Ethiopia | 7.2% | 6.2% |
| 🌍 World | 3.2% | 3.2% |
China and India are forecasted to maintain relatively high growth rates in 2024 at 4.6% and 6.8% respectively, but compared to the previous year, China is growing 0.6 percentage points slower while India is an entire percentage point slower.
On the other hand, four G7 nations are set to grow faster than last year, which includes Germany making its comeback from its negative real GDP growth of -0.3% in 2023.
Faster Growth for BRICS than G7 Nations
Despite mostly lower growth forecasts in 2024 compared to 2023, BRICS nations still have a significantly higher average growth forecast at 3.6% compared to the G7 average of 1%.
While the G7 countries’ combined GDP is around $15 trillion greater than the BRICS nations, with continued higher growth rates and the potential to add more members, BRICS looks likely to overtake the G7 in economic size within two decades.
BRICS Expansion Stutters Before October 2024 Summit
BRICS’ recent expansion has stuttered slightly, as Argentina’s newly-elected president Javier Milei declined its invitation and Saudi Arabia clarified that the country is still considering its invitation and has not joined BRICS yet.
Even with these initial growing pains, South Africa’s Foreign Minister Naledi Pandor told reporters in February that 34 different countries have submitted applications to join the growing BRICS bloc.
Any changes to the group are likely to be announced leading up to or at the 2024 BRICS summit which takes place October 22-24 in Kazan, Russia.
Get the Full Analysis of the IMF’s Outlook on VC+
This visual is part of an exclusive special dispatch for VC+ members which breaks down the key takeaways from the IMF’s 2024 World Economic Outlook.
For the full set of charts and analysis, sign up for VC+.
-

 Markets1 week ago
Markets1 week agoU.S. Debt Interest Payments Reach $1 Trillion
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Countries2 weeks ago
Countries2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoThe Smallest Gender Wage Gaps in OECD Countries