Misc
Map: Visualizing Every Ship at Sea in Real-Time
The ocean is a big place, which makes it a pretty difficult thing to wrap our brains around.
It covers over 70% of the Earth’s surface, is home to millions of species of life, and it makes up 97% of all water on the planet. But, with this massive size and ubiquity also comes a significant challenge for humans interested in trade: it must be constantly traversed in order for us to move goods around.
As a result, millions of people hit the high seas each day to get cargo from one place to another. The vessels used range from tiny sailboats to massive oil tankers, some of which can get up to four football fields in length.
Every Ship at Sea
We previously posted an interactive map of shipping routes that used 250 million data points to show how boats moved across the ocean.
Today, in a similar vein, we highlight a website that tracks the world’s ships in real-time, providing a unique picture of what is happening at sea. Below is a screenshot from MarineTraffic and going there will allow you to see all major ships in real-time as they voyage around the Deep Blue Sea.
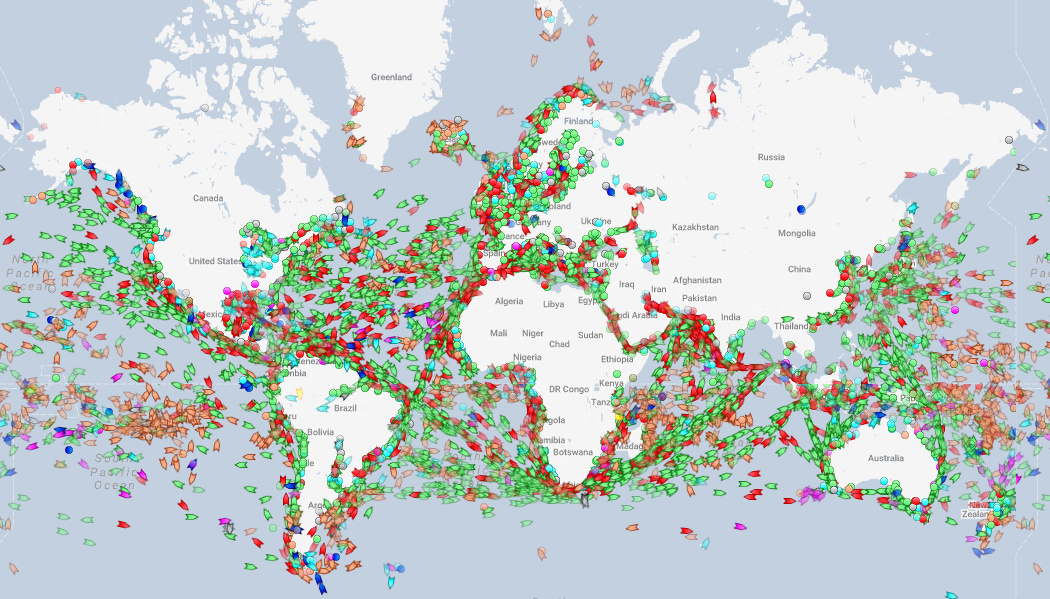
You may be wondering, does this really show every ship at sea?
Well, it might not catch your Uncle Steve’s sailboat off the coast of Florida, but this map will show all major commercial vessels. Any oil tanker, cargo vessel, cruise ship, or fishing boat can be spotted, and it makes for some interesting observations if you know where to look.
A Look at Oil Chokepoints
Upon loading the real-time map, the first thing we did was adjust the filters to only show oil tankers.
After all, we know that every day, about 18.5 million barrels transit through the Strait of Hormuz between Iran and Oman, and 16 million barrels go through the Strait of Malacca between Indonesia and Malaysia.
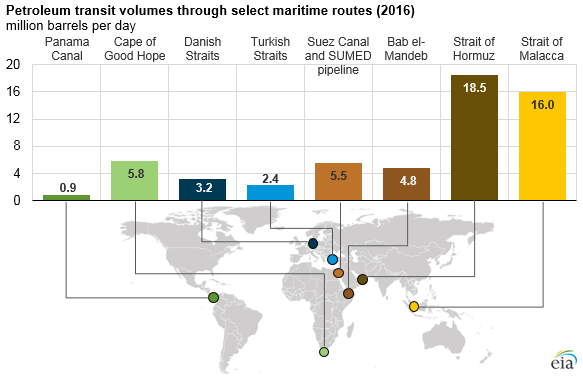
Here’s a screenshot of the Strait of Hormuz, showing only oil tankers. (Dots are tankers that are not moving, while arrows represent tankers that are currently on course.)
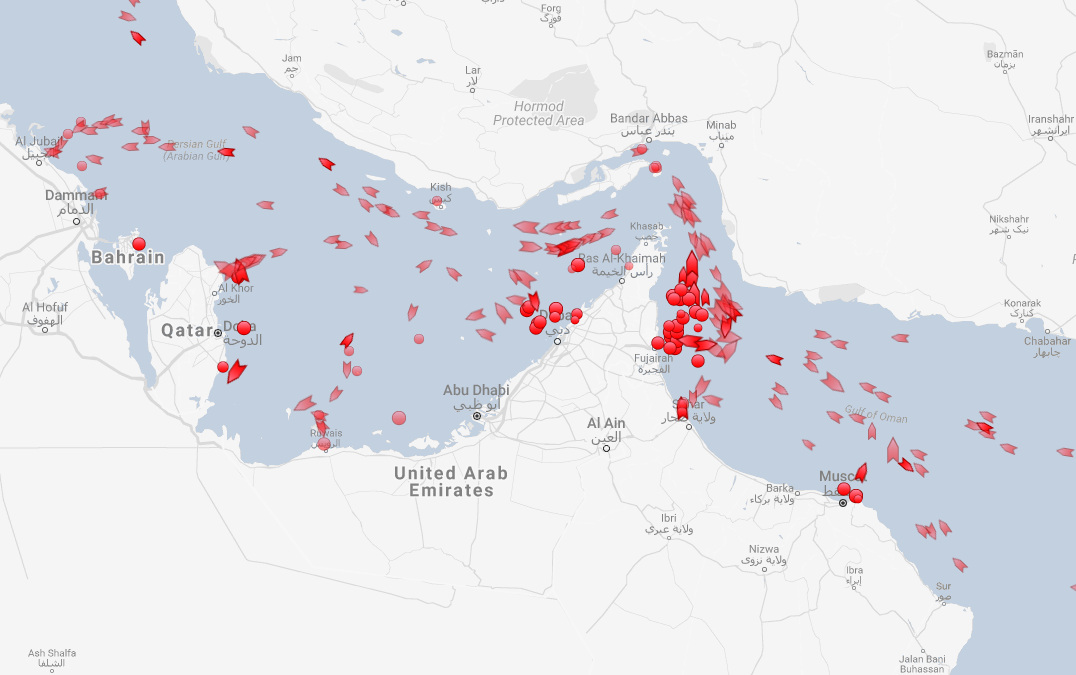
And here are the ships going through the Strait of Malacca, which at its narrowest point is only 1.7 miles (2.7 km) wide.
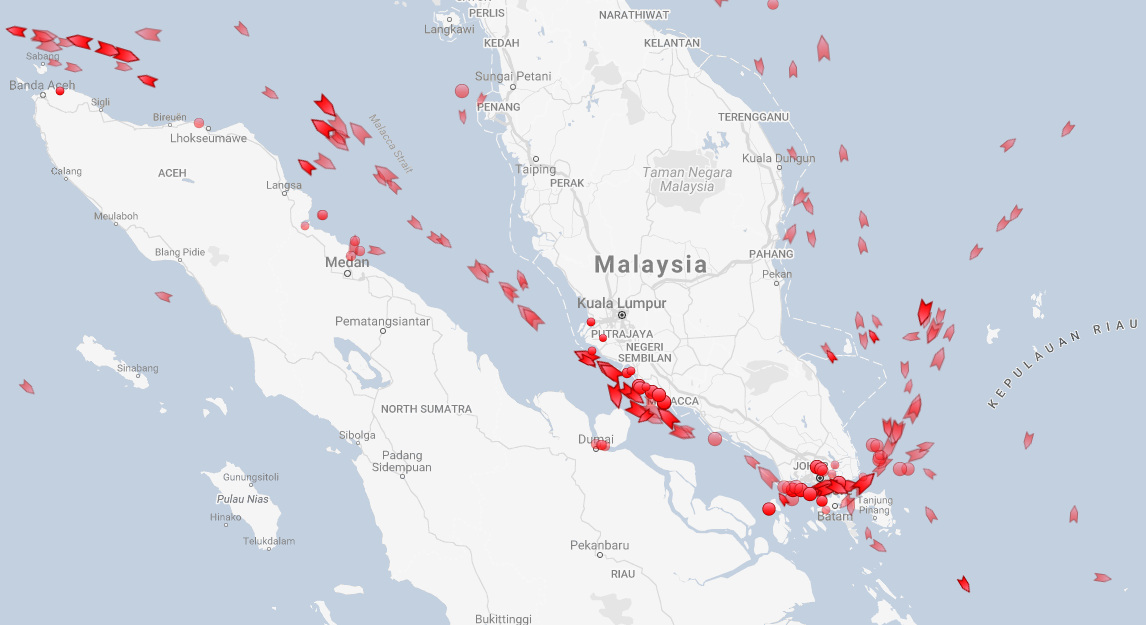
If you want to get oil from the Persian Gulf to the South China Sea, this strait is vital – otherwise a big ship must detour thousands of miles around the Indonesian islands of Sumatra and Java to find the next suitable waterway.
Coast of Somalia
Compare those above straits to the coast off of Somalia, where piracy and hydrocarbon theft are major concerns.
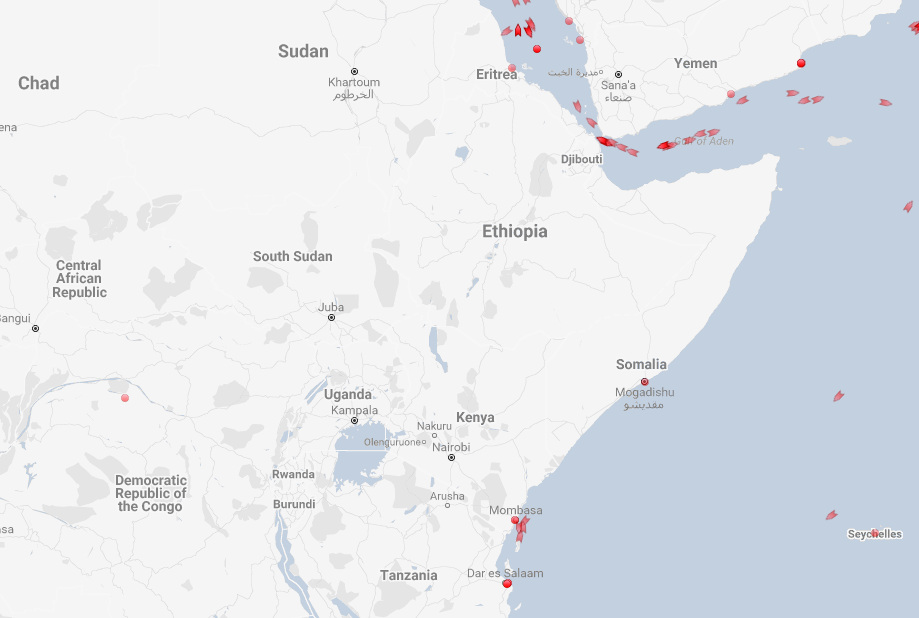
All is pretty quiet, aside from the one daring tanker that is about 500 miles (800 km) east of Mogadishu.
Antarctic Cruises
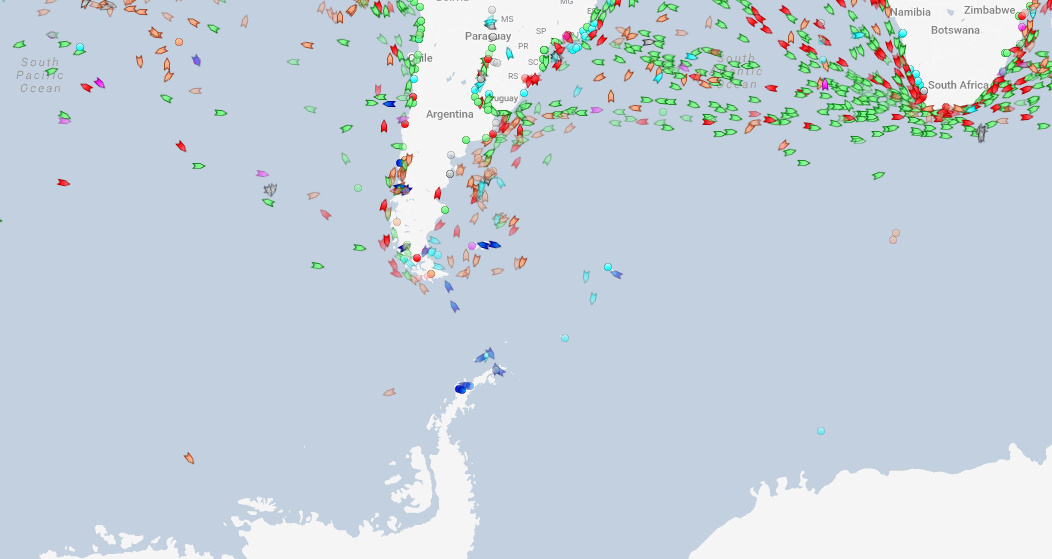
One other easy observation?
It’s the few passenger boats hanging around the Antarctic Peninsula – which is the part of the continent closest to Argentina and a destination for cruise ships.
If you have a chance, check out the live map for yourself and play around with the filters. It’s also interesting to see what’s happening in your local waters, as well.
Politics
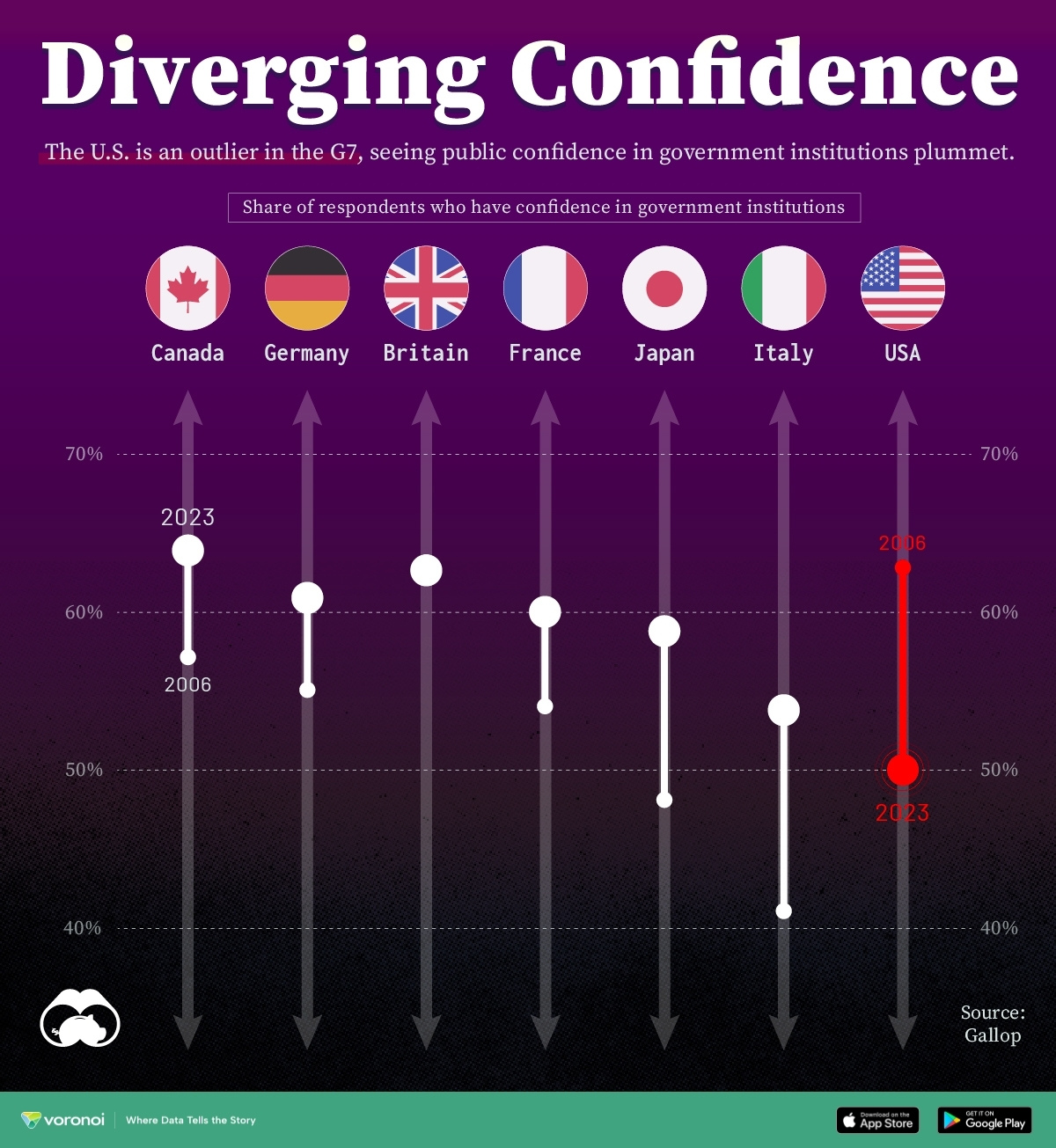
Charted: Trust in Government Institutions by G7 Countries
How much do you trust the government and its various institutions? We look at data for G7 countries for the time period of 2006-2023.
Trust in Government Institutions by G7 Countries
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
How much do you trust the government, and its various institutions?
It’s likely that your level of confidence probably depends on a wide range of factors, such as perceived competency, historical context, economic performance, accountability, social cohesion, and transparency.
And for these same reasons, trust levels in government institutions also change all the time, even in the world’s most developed countries: the G7.
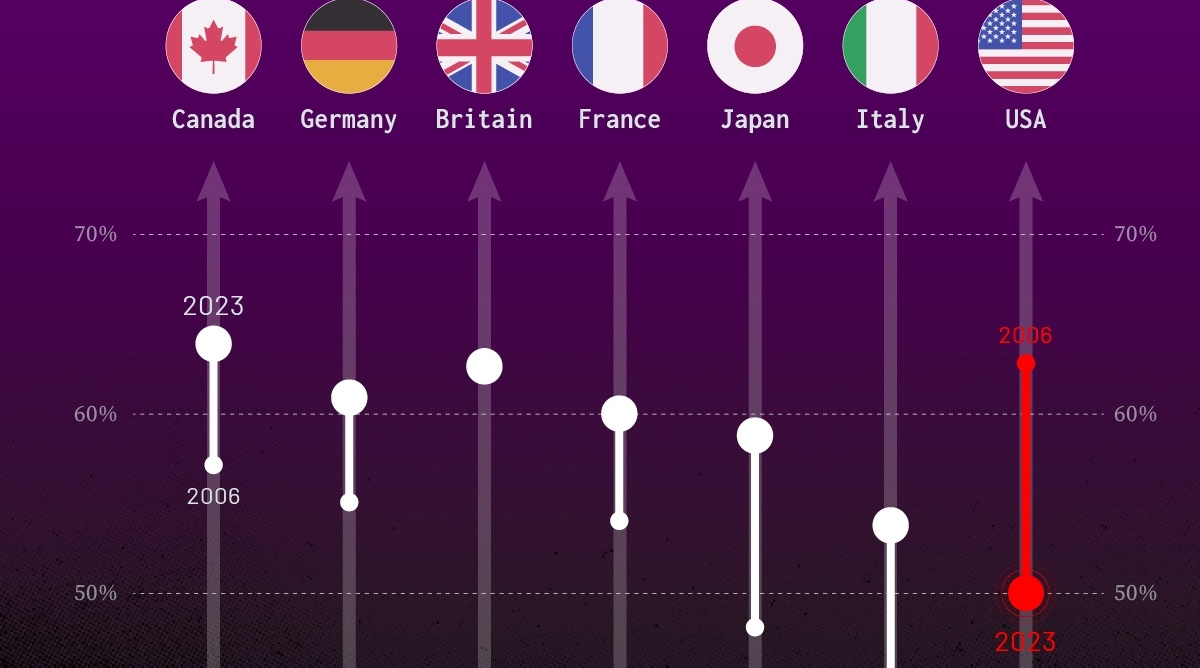
Confidence in Government by G7 Countries (2006-2023)
This chart looks at the changes in trust in government institutions between the years 2006 and 2023, based on data from a multi-country Gallup poll.
Specifically, this dataset aggregates confidence in multiple national institutions, including the military, the judicial system, the national government, and the integrity of the electoral system.
| Country | Confidence (2006) | Confidence (2023) | Change (p.p.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Canada | 57% | 64% | +7 |
| Britain | 63% | 63% | +0 |
| Germany | 55% | 61% | +6 |
| France | 54% | 60% | +6 |
| Japan | 48% | 59% | +11 |
| Italy | 41% | 54% | +13 |
| United States | 63% | 50% | -13 |
What’s interesting here is that in the G7, a group of the world’s most developed economies, there is only one country bucking the general trend: the United States.
Across most G7 countries, confidence in institutions has either improved or stayed the same between 2006 and 2023. The largest percentage point (p.p.) increases occur in Italy and Japan, which saw +13 p.p. and +11 p.p. increases in trust over the time period.
In the U.S., however, confidence in government institutions has fallen by 13 p.p. over the years. What happened?
Key Figures on U.S. Trust in Institutions
In 2006, the U.S. was tied with the UK as having the highest confidence in government institutions, at 63%.
But here’s where the scores stand in 2023, across various institutions:
| 🇺🇸 Institutions | Confidence (2023) |
|---|---|
| Military | 81% |
| Judiciary | 42% |
| National Government | 30% |
| Elections | 44% |
| Overall | 49% |
Based on this data, it’s clear that the U.S. lags behind in three key indicators: confidence in the national government, confidence in the justice system, and confidence in fair elections. It ranked in last place for each indicator in the G7.
One other data point that stands out: despite leading the world in military spending, the U.S. is only the third most confident in its military in the G7. It lags behind France (86%) and the United Kingdom (83%).
-

 Wealth6 days ago
Wealth6 days agoCharted: Which City Has the Most Billionaires in 2024?
-

 Mining2 weeks ago
Mining2 weeks agoGold vs. S&P 500: Which Has Grown More Over Five Years?
-

 Uranium2 weeks ago
Uranium2 weeks agoThe World’s Biggest Nuclear Energy Producers
-

 Education2 weeks ago
Education2 weeks agoHow Hard Is It to Get Into an Ivy League School?
-

 Debt2 weeks ago
Debt2 weeks agoHow Debt-to-GDP Ratios Have Changed Since 2000
-
 Sports2 weeks ago
Sports2 weeks agoThe Highest Earning Athletes in Seven Professional Sports
-

 Science2 weeks ago
Science2 weeks agoVisualizing the Average Lifespans of Mammals
-

 Brands1 week ago
Brands1 week agoHow Tech Logos Have Evolved Over Time